Dual stream graph augmented transformer model integrating BERT and GNNs for context aware fake news detection
- PMID: 40659626
- PMCID: PMC12259997
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05586-w
Dual stream graph augmented transformer model integrating BERT and GNNs for context aware fake news detection
Abstract
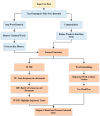
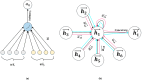
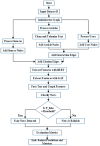
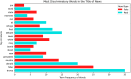
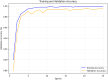
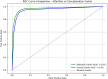
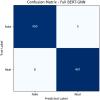
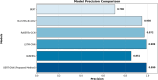
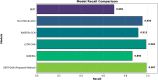
The rapid proliferation of misinformation across digital platforms has highlighted the critical need for advanced fake news detection mechanisms. Traditional methods primarily rely on textual analysis, often neglecting the structural patterns of news dissemination, which play a crucial role in determining credibility. To address this limitation, this study proposes a Dual-Stream Graph-Augmented Transformer Model, integrating BERT for deep textual representation and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to model the propagation structure of misinformation. The objective is to enhance fake news detection by leveraging both linguistic and network-based features. The proposed method employs Graph Attention Networks (GAT) and Graph Transformers to extract contextual relationships, while an attention-based fusion mechanism effectively integrates textual and graph embeddings for classification. The model is implemented using PyTorch and Hugging Face Transformers, with experiments conducted on the FakeNewsNet dataset, which includes news articles, user interactions, and source metadata. Evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and AUC-ROC indicate superior performance, with an accuracy of 99%, outperforming baseline models such as Bi-LSTM and RoBERTa-GCN. The study concludes that incorporating graph-based propagation features significantly improves fake news detection, providing a robust, scalable, and context-aware solution. Future enhancements will focus on refining credibility assessment mechanisms and extending the model to support multilingual and multimodal misinformation detection across diverse digital platforms.
Keywords: BERT; Context-Aware analysis; Fake news detection; Graph neural networks; Transformer model.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent to publish: All the authors are permitted to Consent to publish.
Figures








Similar articles
-
A fake news detection model using the integration of multimodal attention mechanism and residual convolutional network.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20544. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05702-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596197 Free PMC article.
-
Semantic knowledge graph fusion for fake news detection: Unifying content-based features and evidence-based analysis in the COVID-19 infodemic.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 1;20(7):e0321919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321919. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40591693 Free PMC article.
-
Trajectory-Ordered Objectives for Self-Supervised Representation Learning of Temporal Healthcare Data Using Transformers: Model Development and Evaluation Study.JMIR Med Inform. 2025 Jun 4;13:e68138. doi: 10.2196/68138. JMIR Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 40465350 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing respiratory disease diagnosis: A deep learning and vision transformer-based approach with a novel X-ray dataset.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Aug;194:110501. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.110501. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40494170
References
-
- Alghamdi, J., Luo, S. & Lin, Y. A comprehensive survey on machine learning approaches for fake news detection. Multimed Tools Appl.83 (17), 51009–51067 (2024).
-
- Agarwal, A., Singh, Y. P. & Rai, V. Deciphering Deception: Unmasking Fake News in Multilingual Contexts, in IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (IC2PCT), IEEE, 2024, pp. 807–812., IEEE, 2024, pp. 807–812. (2024).
-
- Singh, M. K., Ahmed, J., Alam, M. A., Raghuvanshi, K. K. & Kumar, S. A comprehensive review on automatic detection of fake news on social media. Multimed Tools Appl.83 (16), 47319–47352 (2024).
-
- Olivera-Figueroa, L. A. & Bhattacharjee, U. The impact of misinformation, conspiracy theories, and fake news during the COVID-19 pandemic: what artificial intelligence can contribute to detect and mitigate their proliferation, in Handbook of Media Psychology: the Science and the Practice, Springer, 227–241. (2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

