Scaffold-hopping for molecular glues targeting the 14-3-3/ERα complex
- PMID: 40659654
- PMCID: PMC12260087
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61176-4
Scaffold-hopping for molecular glues targeting the 14-3-3/ERα complex
Abstract
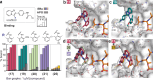
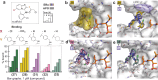
Molecular glues, small molecules that bind cooperatively at a protein-protein interface, have emerged as powerful modalities for the modulation of protein-protein interactions (PPIs) and "undruggable" targets. The systematic identification of new chemical matter with a molecular glue mechanism of action remains a significant challenge in drug discovery. Here, we present a scaffold hopping approach, using as a starting point our previously developed molecular glues for the native 14-3-3/estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) complex. The novel, computationally designed scaffold is based on the Groebke-Blackburn-Bienaymé multi-component reaction (MCR), leading to drug-like analogs with multiple points of variation, thus enabling the rapid derivatization and optimization of the scaffold. Structure-activity relationships (SAR) are developed using orthogonal biophysical assays, such as intact mass spectrometry, TR-FRET and SPR. Rational structure-guided optimization is facilitated by multiple crystal structures of ternary complexes with the glues, 14-3-3 and phospho-peptides mimicking the highly disordered C-terminus of ERα. Cellular stabilization of 14-3-3/ERα for the most potent analogs is confirmed using a NanoBRET assay with full-length proteins in live cells. Our approach highlights the potential of MCR chemistry, combined with scaffold hopping, to drive the development and optimization of unprecedented molecular glue scaffolds.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Michelle R. Arkin, Christian Ottmann, and Luc Brunsveld are co-founders of Ambagon Therapeutics. M.K., M.Z., M.F., C.G.N,. and M.R.A. are co-inventors on a patent application related to this work. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Andrei, S. A. et al. Stabilization of protein-protein interactions in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov.12, 925–940 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Bier, D., Thiel, P., Briels, J. & Ottmann, C. Stabilization of Protein–Protein Interactions in chemical biology and drug discovery. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol.119, 10–19 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Arkin, M. R. & Wells, J. A. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein–protein interactions: progressing towards the dream. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.3, 301–317 (2004). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM147696/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030265/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- Gravity program 024.001.035/Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research | Stichting voor de Technische Wetenschappen (Technology Foundation STW)
- GM147696/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

