Identification of host cell surface proteins inhibiting furin dependent proteolytic processing of viral glycoproteins
- PMID: 40659811
- PMCID: PMC12259872
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-11164-x
Identification of host cell surface proteins inhibiting furin dependent proteolytic processing of viral glycoproteins
Abstract
Proteolytic cleavage by furin-like proteases is a crucial first step in the posttranslational modification of various glycoproteins found in enveloped emerging viruses, such as SARS-CoV-2 and highly pathogenic avian influenza A viruses (IAV). Here, we explored the capacity of host cell proteins identified by cell surface proximity ligation to limit the proteolytic cleavage of the SARS-CoV-2 spike and the IAV H5N1 hemagglutinin (HA). When co-expressed with recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Prom1, Axl, and Ly75 suppress its proteolytic cleavage, whereas cleavage of HA was only reduced by Prom1. Co-immunoprecipitation assays suggest that Axl and Prom1 may form a complex with furin. Alteration of Prom1, Axl and Ly75 expression levels in Calu3 cells affected entry of SARS-CoV-2 S pseudotyped VLP and to a lesser extent, SARS-CoV-2 virions. In contrast, Prom1 levels did not affect entry of H5N1 VLPs or H5N1 virions. Our data highlight the differential capacity of SARS-CoV-2 and IAV H5N1 to cope with newly identified host restriction factors of furin activity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Figures
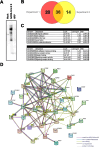
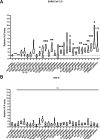



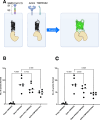


References
-
- WHO COVID-19 dashboard (2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

