N-doped carbon dots for dual-modality NIR fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy
- PMID: 40660215
- PMCID: PMC12261557
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03497-6
N-doped carbon dots for dual-modality NIR fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy
Abstract
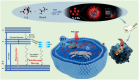
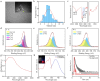
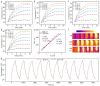
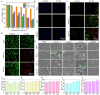
Photothermal therapy (PTT), a rapidly advancing non-invasive cancer treatment modality, utilizes photothermal agents to convert light energy into thermal energy, enabling precise and localized destruction of cancer cells. Recent developments have focused on photothermal agents operating in the second near-infrared (NIR-II) biological window (1000–1350 nm), which offer enhanced tissue penetration depth and improved therapeutic precision for deep-seated tumors while minimizing collateral damage to healthy tissues. In this study, we developed a novel class of nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) through a facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis approach. The synthesized N-CDs demonstrate remarkable dual functionality, exhibiting both superior photothermal performance and fluorescence imaging capabilities within the NIR region, thereby enabling simultaneous tumor diagnosis and therapy. These N-CDs display exceptional biocompatibility and achieve impressive photothermal conversion efficiencies of 31.25% and 27.12% under 808 nm and 1060 nm laser irradiation, respectively, with corresponding temperature changes of 42.8 ℃ and 39.7 ℃ in vitro. Notably, the N-CDs exhibit a strong fluorescence emission peak at 660 nm, approaching the NIR-I window, which facilitates high-contrast bioimaging. In vivo studies confirmed the therapeutic efficacy of N-CDs, demonstrating cancer cell ablation under both 808 nm and 1060 nm laser irradiation, coupled with accurate tumor localization capabilities. The unique combination of intense fluorescence emission, exceptional photothermal conversion efficiency, and outstanding biocompatibility positions these N-CDs as a highly promising theranostic platform for integrated cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12951-025-03497-6.
Keywords: Bioluminescence imaging; Carbon Dots; Near-infrared II window; Photothermal therapy; Tumor elimination.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal were purchased from the Laboratory Animal Center of Shanxi Medical University (SYXK 2024-0007). The animal experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of Taiyuan University of Technology. The animal experimental protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the International Standards for Animal Welfare (Approval No.: TYUT-202105001). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
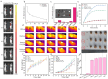
Similar articles
-
Nitrogen and Boron Dual-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Near-Infrared Second Window Imaging and Photothermal Therapy.Appl Mater Today. 2019 Mar;14:108-117. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2018.11.011. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Appl Mater Today. 2019. PMID: 31538108 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon dots-mediated synthesis of gold nanodendrites with extended absorption into NIR-II window for in vivo photothermal therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 May 9;21(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01887-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37161467 Free PMC article.
-
Near-infrared-II photothermal ultra-small carbon dots promoting anticancer efficiency by enhancing tumor penetration.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Jun 15;616:595-604. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.02.083. Epub 2022 Feb 22. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 35231703
-
Applications of nanotheranostics in the second near-infrared window in bioimaging and cancer treatment.Nanoscale. 2024 Dec 5;16(47):21697-21730. doi: 10.1039/d4nr03058c. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 39508492 Review.
-
Molecular fluorophores for in vivo bioimaging in the second near-infrared window.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Jul;49(9):3226-3246. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05688-x. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35088125
References
-
- Liu HH, Gao CJ, Xu PJ, Li YS, Yan XX, Guo XL, Wen CC, Shen XC. Biomimetic gold nanorods-manganese porphyrins with surface-enhanced Raman scattering effect for photoacoustic imaging-guided photothermal/photodynamic therapy. SMALL. 2024;20(42):e2401117. - PubMed
-
- Geng B, Yang D, Pan D, Wang L, Zheng F, Shen W, Zhang C, Li X. NIR-responsive carbon Dots for efficient photothermal cancer therapy at low power densities. Carbon. 2018;134:153–62.
Grants and funding
- 2023-ZD01, 2020-ZD01/the Open Research Fund Program of Collaborative Innovation Center for Molecular Imaging of Precision Medicine
- 202403021211021/the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province
- 202303021221226/the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province
- 022XM38/the Four "Batches" Innovation Project of Invigorating Medical through Science and Technology of Shanxi Province
- YDZJSX2022A058/Central Leading Local Science and Technology Development Fund Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

