Targeted Inhibition of cGAS/STING signaling induced by aberrant R-Loops in the nucleus pulposus to alleviate cellular senescence and intervertebral disc degeneration
- PMID: 40660286
- PMCID: PMC12261858
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03579-5
Targeted Inhibition of cGAS/STING signaling induced by aberrant R-Loops in the nucleus pulposus to alleviate cellular senescence and intervertebral disc degeneration
Abstract
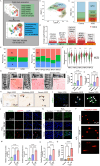
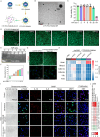
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) is a significant contributor to chronic low back pain and disability worldwide, yet effective treatment options remain limited. Through integrative analysis of single-cell RNA-seq data from intervertebral discs (IVDs), we have firstly uncovered that the aberrant accumulation of R-Loops-a type of triple-stranded nucleic acid structure-can result in the cytoplasmic accumulation of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and activate cGAS/STING signaling and induce cellular senescence in nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) during IVDD. Restoring the R-Loop state significantly mitigated both the activation of the cGAS/STING pathway and NPC senescence. Additionally, we identified ERCC5 as a critical regulator of the R-Loop state and cellular senescence. Thus, we developed an NPC-targeting nano-delivery platform (CTP-PEG-PAMAM) to deliver si-Ercc5 to the NP region of the IVDD. This approach aims to modulate the abnormal R-Loop state and inhibit the activation of cGAS/STING signaling in NPCs for IVDD treatment. CTP-PEG-PAMAM demonstrated excellent targeting capability towards NPCs and NP tissue, and achieved effective silencing of the Ercc5 gene without causing systemic organ complications. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments revealed that CTP-PEG-PAMAM-siERCC5 significantly inhibited cGAS/STING signaling activated by aberrant R-Loops, alleviated cellular senescence and promoting cell proliferation, thereby delayed IVDD in a puncture-induced rat model. In conclusion, the ERCC5-R-Loop-cGAS/STING axis in NPCs represents a promising therapeutic target for delaying IVDD, and the designed CTP-PEG-PAMAM/siRNA complex holds great potential for clinical application in the treatment of IVDD.
Keywords: Cellular senescence; ERCC5; Intervertebral disc degeneration; Nucleus pulposus-specific nano-delivery platform; R-Loops; cGAS/STING.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines set forth by the National Institutes of Health for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and received approval from the Animal Research Committee at our institution. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Therapeutic effects of PDGF-AB/BB against cellular senescence in human intervertebral disc.Elife. 2025 Jul 16;13:RP103073. doi: 10.7554/eLife.103073. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40668091 Free PMC article.
-
PHLDA2 overexpression facilitates senescence and apoptosis via the mitochondrial route in human nucleus pulposus cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway.IUBMB Life. 2024 Oct;76(10):788-802. doi: 10.1002/iub.2829. Epub 2024 May 9. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 38721892
-
Cryptotanshinone attenuates lactate-induced nucleus pulposus cells injury by modulating the STAT3/SIRT3 signaling axis.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:157021. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157021. Epub 2025 Jun 28. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40609385
-
Sirtuins in intervertebral disc degeneration: current understanding.Mol Med. 2024 Mar 29;30(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00811-0. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38553713 Free PMC article.
-
Photoaging: UV radiation-induced cGAS-STING signaling promotes the aging process in skin by remodeling the immune network.Biogerontology. 2025 Jun 20;26(4):123. doi: 10.1007/s10522-025-10268-1. Biogerontology. 2025. PMID: 40542276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Knezevic NN, Candido KD, Vlaeyen J, Van Zundert J, Cohen SP. Low back pain. Lancet. 2021;398(10294):78–92. - PubMed
-
- Han L, Li F, Wu H, Wang W, Chen P, Xia W, et al. Targeting FABP4 to inhibit AGEs-RAGE/NF-κB signalling effectively ameliorates nucleus pulposus dysfunction and angiogenesis in obesity-related intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2025;e70021. Epub ahead of print. 10.1111/cpr.70021. PMID: 40090836. - PubMed
-
- Sun K, et al. The role of nerve fibers and their neurotransmitters in regulating intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;81:101733. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

