Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a potential therapeutic strategy for ferroptosis
- PMID: 40660292
- PMCID: PMC12261762
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-025-04511-2
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a potential therapeutic strategy for ferroptosis
Abstract
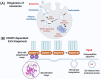
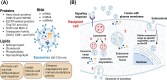
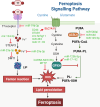
Ferroptosis, a regulated type of cell death directed by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, is associated with a variety of pathological diseases. Recent findings have highlighted the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) in modulating ferroptosis. These nano-sized extracellular vesicles carry bioactive substances, including proteins, lipids, and microRNAs, which regulate vital pathways related to ferroptosis, such as reactive oxygen species production, glutathione metabolism, and lipid peroxidation. Preclinical studies suggest that MSC-Exos can alleviate ferroptosis-induced damage by enhancing antioxidant defenses, mitigating oxidative stress, upregulating anti-ferroptotic regulators, and suppressing lipid peroxidation. Notably, in cancer, MSC-Exos may protect non-malignant tissues from chemotherapy-induced ferroptosis. By exploiting their regenerative and immunomodulatory properties, MSC-Exos offer a promising therapeutic platform for targeting ferroptosis in diverse pathological conditions. This review summarizes the biological and functional characteristics of MSC-Exos, elucidates their roles in ferroptosis regulation across multiple disease models, and discusses current challenges and future directions for clinical translation.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell death; Exosomes; Ferroptosis; Mesenchymal stem cells; Neurodegenerative diseases; Oxidative stress; Regenerative medicine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yan JL, Bao H, Liang, et al. A druglike Ferrostatin-1 analogue as a ferroptosis inhibitor and photoluminescent Indicator. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2025. 10.1002/anie.202502195. e202502195.DOI. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JF, Lin Y, Xiao, et al. Discovery and optimization of 1,2,4-triazole derivatives as novel ferroptosis inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2025;284:117192. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.117192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

