Entheseal Doppler signals in ultrasound are associated with vasodilator drugs and age in patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis
- PMID: 40660310
- PMCID: PMC12261538
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-025-03614-8
Entheseal Doppler signals in ultrasound are associated with vasodilator drugs and age in patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis
Abstract
Background: The ability of modern ultrasound machines to detect signs of enthesitis has increased, yet there is a lack of studies on patients with long-standing radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA). Hence, we aimed to investigate the prevalence and clinical significance of Doppler signals indicative of inflammation in peripheral entheses of patients with long-standing disease.
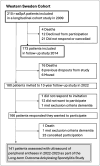
Methods: Patients fulfilling the modified New York criteria for ankylosing spondylitis were included in this cohort study. Peripheral entheses were examined clinically and the presence of focal pain was self-reported on a mannequin. Ultrasound examination of 1692 entheses was performed. Doppler signals were graded from 0 to 3 using color Doppler ultrasound and Smooth Microvascular Imaging. Multivariable linear regression was used to explore factors influencing Doppler signals.
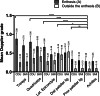
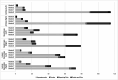
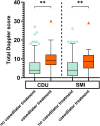
Results: One hundred and forty-one patients were included with, age (mean (SD)) 60 (12) years, symptom duration 34 (12) years, males 57%, and HLA-B27 86%. Overall, 21.3% of patients presented with ≥ 1 active ultrasound enthesitis (Doppler signals combined with hypoechoic tissue). In 4.3% of patients these findings were tender on palpation. Isolated Doppler signals were found in 89.4-97.1% of patients, with the highest mean Doppler grades in the triceps entheses (0.88), and the lowest in the Achilles tendons (0.28). In multivariable linear regression analysis, age (B (95% CI)) (0.01 (0.00; 0.01), p = 0.004), daily NSAIDs (0.15 (0.00; 0.30), p = 0.048), vasodilator drugs 0.16 (0.01; 0.32, p = 0.041), but not AS disease activity score, were associated with total Doppler scores.
Conclusion: The prevalence of asymptomatic entheseal ultrasound Doppler findings was overall high. The use of vasodilator drugs and higher age increased the Doppler scores. No association between disease activity and Doppler scores was found in patients with long-standing disease.
Keywords: Ankylosing spondylitis; Axial spondyloarthritis; Diagnostic imaging; Doppler ultrasonography; Enthesopathy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Swedish ethical review board (597–08, 2021–03484) and performed in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants gave their written informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for axial spondyloarthritis (ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 17;2015(7):CD010952. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010952.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26186173 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and progression of radiographic enthesopathy at hip and pelvis in patients with axial spondyloarthritis based on CT assessment.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):2809-2818. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07535-4. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40516015
-
TNF-alpha inhibitors for ankylosing spondylitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 18;2015(4):CD005468. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005468.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25887212 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour necrosis factor-α inhibitors for ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2016 Feb;20(9):1-334, v-vi. doi: 10.3310/hta20090. Health Technol Assess. 2016. PMID: 26847392 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic determinants of worse sexual experience in male patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a multimodal study.RMD Open. 2025 Jun 25;11(2):e005594. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005594. RMD Open. 2025. PMID: 40562683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Navarro-Compán V, Sepriano A, El-Zorkany B, van der Heijde D. Axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(12):1511–21. - PubMed
-
- McGonagle D, Gibbon W, O’Connor P, Green M, Pease C, Emery P. Characteristic magnetic resonance imaging entheseal changes of knee synovitis in spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(4):694–700. - PubMed
-
- Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(6):777–83. - PubMed
-
- Navarro-Compán V, Boel A, Boonen A, Mease PJ, Dougados M, Kiltz U, et al. Instrument selection for the ASAS core outcome set for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(6):763–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- [VGFOUREG-383071, VGFOUREG-564511, VGFOUREG-754661/Health and Medical Care Committee of the Regional Executive Board, Region Västra Götaland
- [ALFGBG-938395, ALFGBG-965333]/The Swedish state under the agreement between the Swedish government and the county councils, the ALF agreement
- [FAI-2017-0454, FAI-2019-0560, FAI-2022-0883]/king Gustaf Vth 80-year Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

