Short-term clinical effect of total hip replacement in the treatment of sequelae of septic arthritis of the hip: A retrospective study
- PMID: 40660575
- PMCID: PMC12263079
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043269
Short-term clinical effect of total hip replacement in the treatment of sequelae of septic arthritis of the hip: A retrospective study
Abstract
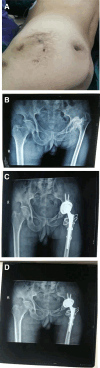
Total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of sequelae of suppurative hip arthritis is very complicated. To observe the short-term efficacy and complications of total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of sequelae of suppurative hip arthritis and to improve the success rate and curative effect of operation, the clinical data of 32 patients with sequelae of suppurative hip arthritis who underwent total hip arthroplasty in our department from June 2013 to December 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. The age of hip suppurative infection was 2 to 17 years, with an average age of (9.8 ± 6.2) years. The average age was (35.2 ± 12.5) years. All the patients were treated by the direct lateral approach (Hardinge approach), and the acetabular and femoral sides were fixed with the biological prosthesis. All the 32 patients were followed up, and 2 patients had sciatic nerve palsy after operation, and the neurological symptoms recovered after conservative treatment for 1 month. One case of subtrochanteric osteotomy nonunion and femoral prosthesis loosening was treated with femoral lengthening stem revision. The clinical symptoms and hip joint activity of all patients were significantly improved after operation. The average Harris score was 43.3 ± 7.2 before operation and 88.6 ± 9.1 at the last follow-up after operation, and the difference was statistically significant (P < .05). The preoperative visual analogue scale was (7.1 ± 1.6) points, and it decreased to (1.1 ± 0.6) points at the last follow-up, and the difference was statistically significant (P < .05). Total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of sequelae of suppurative hip arthritis has a satisfactory short-term effect, which can effectively relieve pain and improve hip joint function after operation.
Keywords: clinical outcomes; sequelae; suppurative hip arthritis; total hip arthroplasty.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What Are the Functional, Radiographic, and Survivorship Outcomes of a Modified Cup-cage Technique for Pelvic Discontinuity?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2149-2160. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003186. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38991223
-
Is 18 F-fluoride PET/CT an Accurate Tool to Diagnose Loosening After Total Joint Arthroplasty?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Mar 1;483(3):415-428. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003228. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39293088
-
[Application of robot-assisted posterolateral approach in complex primary total hip arthroplasty].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Sep 1;63(9):792-798. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20250228-00103. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40734411 Chinese.
-
Total hip replacement and surface replacement for the treatment of pain and disability resulting from end-stage arthritis of the hip (review of technology appraisal guidance 2 and 44): systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2015 Jan;19(10):1-668, vii-viii. doi: 10.3310/hta19100. Health Technol Assess. 2015. PMID: 25634033 Free PMC article.
-
Total hip arthroplasty in active and advanced tubercular arthritis: a systematic review of the current evidence.Int Orthop. 2024 Jan;48(1):79-93. doi: 10.1007/s00264-023-05943-2. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Int Orthop. 2024. PMID: 37668728
References
-
- Jiang W, Xu H, Wang X, et al. Poor performance of monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and fibrinogen when screening for occult infection among patients with sequelae of suppurative hip arthritis before total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2022;46:1929–35. - PubMed
-
- Danilov C, Fernandez FF, Wirth T, Eberhardt O. Relevant factors in the diagnosis of concomitant osteomyelitis in pediatric hip septic arthritis. a series of 41 cases treated by hip arthroscopy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143:1825–32. - PubMed
-
- Zaballa E, Dennison E, Walker-Bone K. Function and employment after total hip replacement in older adults: a narrative review. Maturitas. 2023;167:8–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical