Carnosol attenuates Acinetobacter baumannii virulence by interfering with indole-mediated quorum sensing
- PMID: 40660701
- PMCID: PMC12269709
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2530169
Carnosol attenuates Acinetobacter baumannii virulence by interfering with indole-mediated quorum sensing
Abstract
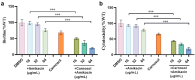
Many bacterial pathogens utilize quorum sensing (QS) signals to modulate the biological functions in a cell density-dependent manner. Acinetobacter baumannii is a harmful pathogen and a major cause of hospital-acquired infections due to its severe drug-resistance and pathogenic nature. Therefore, the development of innovative antibacterial strategies for A. baumannii infections is important. Earlier studies have proved that A. baumannii utilizes N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) and indole signalling systems to modulate its biological functions and virulence. Here, we report that carnosol, which is isolated from Salvia officinalis L. (S. officinalis), inhibited the pathogenicity of A. baumannii by interfering with indole-mediated quorum sensing. Phenotypic and virulence experiments have revealed that carnosol decreased the formation of biofilms, motility, and cytotoxicity of A. baumannii, without affecting its growth rate. Genetic and biochemical analysis results showed that carnosol reduced the regulatory effect of AbiR on the transcription of target genes by inhibiting the binding of AbiR to the promoters of these genes. Our results suggest that the indole QS system of A. baumannii could be used as a new target and that carnosol might be developed as a new anti-virulence agent against A. baumannii infections.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; carnosol; indole; quorum sensing; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





Similar articles
-
CRISPR/Cas9-targeted smpB mutation revealing roles in biofilm formation, motility, and antibiotic susceptibility in Acinetobacter baumannii.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 4;20(8):e0329638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329638. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40758696 Free PMC article.
-
The Response of Acinetobacter baumannii to Hydrogen Sulfide Reveals Two Independent Persulfide-Sensing Systems and a Connection to Biofilm Regulation.mBio. 2020 Jun 23;11(3):e01254-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01254-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32576676 Free PMC article.
-
A cell-cell communication signal from Enterobacter cloacae interfering with the signaling systems and virulence in Shigella sonnei.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jun 18;91(6):e0051025. doi: 10.1128/aem.00510-25. Epub 2025 May 12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40353654 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum-sensing system in Acinetobacter baumannii: a potential target for new drug development.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Jan;128(1):15-27. doi: 10.1111/jam.14330. Epub 2019 Jun 26. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31102552 Review.
-
Quorum sensing inhibitors (QSIs): a patent review (2019-2023).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2025 Jul;35(7):657-673. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2025.2491382. Epub 2025 Apr 16. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2025. PMID: 40219759 Review.
References
-
- Swe swe-Han K, Mlisana KP, Pillay M.. Analysis of clinical and microbiological data on Acinetobacter baumannii strains assist the preauthorization of antibiotics at the patient level for an effective antibiotic stewardship program. J Infect Public Health. 2017;10(5):608–616. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2017.01.014 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
