Spent Media Management Pathways for PFAS Treatment Applications
- PMID: 40660761
- PMCID: PMC12260480
- DOI: 10.1002/wer.70130
Spent Media Management Pathways for PFAS Treatment Applications
Abstract
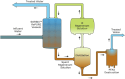
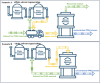
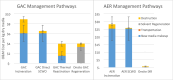
Removing PFAS from water is increasingly needed to comply with evolving regulations in multiple industries, including drinking water production, municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, and contaminated site remediation. This change is driving increased use of adsorptive media to remove PFAS from drinking water. Granular activated carbon (GAC) and anion exchange resin (AER) are the two predominantly applied media used to separate PFAS from water. Both technologies produce PFAS-laden spent media that requires downstream management, with significant operating costs and regulatory uncertainty. Once GAC or AER media is spent, it can be physically changed out from treatment vessels or regenerated in place. Spent media can be managed through existing offerings like incineration or GAC reactivation or through emerging offerings like supercritical water oxidation (SCWO). Spent regenerant can be recovered and reused, with concentrated PFAS-laden liquid managed through offsite incineration or emerging PFAS destruction methods. Both offsite GAC reactivation and onsite regeneration of either AER or GAC have the potential to reduce operating costs and energy use relative to single-use media procurement and disposal.
Keywords: anion exchange resin (AER); emerging contaminants; granular activated carbon (GAC); industrial pretreatment; per‐ and poly‐fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS); spent media.
© 2025 The Author(s). Water Environment Research published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Water Environment Federation.
Conflict of interest statement
Tiffany Stegner, Maggie Thompson, Sudhakhar Viswanathan, and Brian Pinkard are employees of companies that develop, demonstrate, and sell PFAS treatment technologies and/or services in the area of spent media management. Katie Wolohan and Don Richard are consultants at a company that has done work for and with similar technology companies in the past.
Figures



References
-
- 40 CFR Part 131 Subpart B—Establishment of Water Quality Standards . 2024. https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title‐40/chapter‐I/subchapter‐D/part‐131/su....
-
- AWWA . 2018. B605–18 Reactivation of Granular Activated Carbon. American Water Works Association.
-
- Bailey, C. 2021. “Final Report: Plasma‐Enhancement of Absorbers for Improved Removal of PFOS and PFOA From Water.” https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncer_abstracts/index.cfm/fuseaction/display.highli....
-
- Barr Engineering Co. Hazen and Sawyer . 2023. “Evaluation of Current Alternatives and Estimated Cost Curves for PFAS Removal and Destruction From Municipal Wastewater, Biosolids, Landfill Leachate, and Compost Contact Water.” https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/c‐pfc1‐26.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

