This is a preprint.
Brain-derived extracellular vesicle microRNAs in Lewy body and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40661348
- PMCID: PMC12258949
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.06.656900
Brain-derived extracellular vesicle microRNAs in Lewy body and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
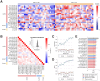
Introduction: Robust plasma-based biomarkers to distinguish Lewy body disease (LBD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) are currently lacking. We applied track-etch magnetic nanopore (TENPO) sorting for enrichment of brain-derived extracellular vesicle (EV) signatures as potential biomarkers to address this gap.
Methods: We analyzed plasma from 137 autopsy-confirmed patients [30 LBD, 31 AD, 30 AD/LBD, 19 AD with amygdala Lewy bodies (AD/ALB), and 27 controls], sequencing miRNAs from TENPO-isolated GluR2-positive (neuron-enriched) and GLAST-positive (astrocyte-enriched) EVs, and measuring plasma proteins (Aβ40, Aβ42, tau, p-Tau181, p-Tau231) via SIMOA.
Results: We identified 16 GluR2+, 8 GLAST+, and 4 protein biomarkers with differential expression (false discovery rate-corrected P value < .1) between LBD and AD. A multimodal 15-feature panel classified LBD versus AD with 10-fold crossvalidated accuracy = 0.95 and area under the curve (AUC) = 0.96.
Discussion: Brain-derived EVs offer accurate and accessible miRNA biomarkers for the differential diagnosis of LBD and AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Lewy body disease; astrocyte; extracellular vesicles; microRNA; microfluidics; neurodegenerative dementia; neuron; plasma biomarkers; protein biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT David Issadore is a founder and holds shares in Chip Diagnostics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Prasad S, Katta MR, Abhishek S, Sridhar R, Valisekka SS, Hameed M, et al. Recent advances in Lewy body dementia: A comprehensive review. Disease-aMonth. 2023;69(5):101441. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
