Matrix Stiffness Regulates TGFβ1-Induced αSMA Expression via a G9a-LATS-YAP Signaling Cascade
- PMID: 40661662
- PMCID: PMC12256985
- DOI: 10.1096/fba.2025-00117
Matrix Stiffness Regulates TGFβ1-Induced αSMA Expression via a G9a-LATS-YAP Signaling Cascade
Abstract
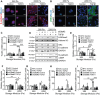
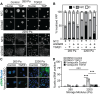
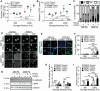
Extracellular matrix stiffness is enhanced in cancer and fibrosis; however, there is limited knowledge on how matrix mechanics modulate expression and signaling of the methyltransferase G9a. Here, we show that matrix stiffness and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 signaling together regulate G9a expression and the levels of the histone mark H3K9me2. Suppressing the activity and expression of G9a attenuates TGFβ1-induced alpha smooth muscle actin (αSMA) and N-cadherin expression and cell morphology changes in mammary epithelial cells cultured on stiff substrata. Knockdown of G9a increases the expression of large tumor suppressor kinase 2 (LATS2) and decreases the nuclear localization of yes associated protein (YAP). Furthermore, inhibition of LATS promotes an increase in YAP nuclear localization and αSMA expression, while inhibition of YAP attenuates αSMA expression. Overall, our findings indicate that a G9a-LATS-YAP signaling cascade regulates mammary epithelial cell response to matrix stiffness and TGFβ1.
Keywords: epigenomics; epithelial cells; extracellular matrix; histone methyltransferases; hydrogels; mammary gland.
© 2025 The Authors. FASEB BioAdvances published by The Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Trpv4-mediated mechanotransduction regulates the differentiation of valvular interstitial cells to myofibroblasts: implications for aortic valve stenosis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 May 1;328(5):C1558-C1570. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00977.2024. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40203884 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Matrix Stiffness and TGFβ2 Regulate YAP/TAZ Activity in Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 1;10:844342. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.844342. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35300422 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular pH dynamics respond to extracellular matrix stiffening and mediate vasculogenic mimicry through β-catenin.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 25:2024.06.04.597454. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.04.597454. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 38895391 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
EORTC guidelines for the use of erythropoietic proteins in anaemic patients with cancer: 2006 update.Eur J Cancer. 2007 Jan;43(2):258-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2006.10.014. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Eur J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17182241
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paszek M. J., Zahir N., Johnson K. R., et al., “Tensional Homeostasis and the Malignant Phenotype,” Cancer Cell 8 (2005): 241–254. - PubMed
-
- Sankhe C. S., Sacco J. L., and Gomez E. W., “Biophysical Regulation of TGFβ Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment,” in Engineering and Physical Approaches to Cancer, ed. Wong I. Y. and Dawson M. R. (Springer International Publishing, 2023), 159–200.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
