A Comprehensive Review on the Molecular Mechanism of Lycopene in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 40661795
- PMCID: PMC12256281
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70608
A Comprehensive Review on the Molecular Mechanism of Lycopene in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
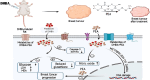
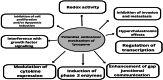
The continuous progression of cancerous severity due to the interaction of physical (ultraviolet radiation), chemical (smoking, mycotoxins, and heavy metals), and biological (microbial populations) carcinogens inspired scientists to develop a correlation between active therapeutic agents and cancer proliferation. This review highlights the molecular mechanism by which lycopene imparts its anticancerous role, focusing on clinical and animal trials to validate its effectiveness. The antioxidant profile of lycopene promotes anticancerous properties that reduce cancer prevalence by activating cell signaling pathways and gene expression (involved in cancer cell proliferation). Lycopene's anti-inflammatory properties suppresses the tumor growth and development-promoting pathways, such as the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. The anticancer property of lycopene is also evidenced by its inhibitory potential of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway that is involved in cancer cell modulation and propagation. Lycopene also suppresses and neutralizes oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced DNA damage, preventing gene mutation. Inflammation-induced cell death is mitigated by lycopene's anti-inflammatory potential that lowers the expression of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). Several clinical and randomized control trials have revealed the effect of lycopene supplementation in the management of cancer, including breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, colon cancer, ovarian cancer, skin cancer, oral cancer, liver cancer, gastric cancer, and kidney cancer, by lessening prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels. These studies also accentuate certain limitations that need further trials to evaluate the long-term consequences of lycopene supplementations and their specific effective dose.
Keywords: DNA damage; PSA levels; anticancer; antioxidants; anti‐inflammatory; cancer cell modulation; lycopene; oxidative stress.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adetunji, C. O. , Akram M., Mtewa A. G., et al. 2021. “Biochemical and Pharmacotherapeutic Potentials of Lycopene in Drug Discovery.” In Preparation of Phytopharmaceuticals for the Management of Disorders, 307–360. Academic Press.
-
- Agah, S. , Akbari A., Sadeghi E., et al. 2021. “Resveratrol Supplementation and Acute Pancreatitis: A Comprehensive Review.” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 137: 111268. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous