Exploring the diversity and genomics of cultivable Bacillus-related endophytic bacteria from the medicinal plant Galium aparine L
- PMID: 40661978
- PMCID: PMC12256460
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1612860
Exploring the diversity and genomics of cultivable Bacillus-related endophytic bacteria from the medicinal plant Galium aparine L
Abstract
Introduction: Endophytes are crucial partners that contribute to the plants' health and overall wellbeing. Apart from the elucidation of the relationship between plants and their microbiota, the metabolic potential of endophytes is also of a special interest. Therefore, it is crucial to isolate and taxonomically identify endophytes, as well as to investigate their genomic potential to determine their significance in plant health and potential as bioactive metabolite producers for industrial application.
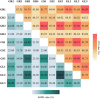
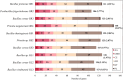
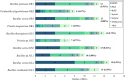
Methods: In this study, we isolated ten endophytic bacterial strains from different tissues of medicinal plant Galium aparine L. and performed de novo assembly of their genomes using short and long reads. Comparative genomic analysis was conducted to assess the accurate taxonomic identification of the strains. The investigation also focused on the presence of mobile genetic elements and their significance concerning endophytic lifestyles. We performed functional annotation of coding sequences, particularly targeted genes that encode carbohydrate enzymes and secondary metabolites within gene clusters.
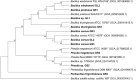
Results: Through sequencing using two complementary methods, we obtained 10 bacterial genomes, ranging in size, coding density and number of mobile genetic elements. Our findings provide a first insight into the cultivable bacterial community of the medicinal plant Galium aparine L., their genome biology, and potential for producing valuable bioactive metabolites. Obtained whole genome sequences allowed for complete phylogenetic analysis, which revealed crucial insights into the taxonomic status of bacteria and resulted in the discovery of two putatively novel bacterial species from the Bacillus and Priestia genera, suggesting that plants are hiding a reservoir of novel species with potentially useful properties and unknown mechanisms related to their relationship with plant host.
Keywords: Galium aparine L.; bacterial endophytes; genome mining; mobile genetic elements; phylogenetics; plant microbiome; secondary metabolites.
Copyright © 2025 Rutkowska, Daroch and Marchut-Mikołajczyk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alcock B. P., Huynh W., Chalil R., Smith K. W., Raphenya A. R., Wlodarski M. A., et al. (2023). CARD 2023: Expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 51 D690–D699. 10.1093/nar/gkac920 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Snafi A. E. (2018). Chemical constituents and medical importance of galium aparine - a review. Indo Am. J. Pharmaceut. Sci. 05 1739–1744. 10.5281/zenodo.1210517 - DOI
-
- Andrews S. (2010). FastQC: A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Cambridge: Babraham Bioinformatics.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

