Screening of host proteins interacting with the African swine fever virus outer membrane protein CD2v
- PMID: 40661982
- PMCID: PMC12256527
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1585335
Screening of host proteins interacting with the African swine fever virus outer membrane protein CD2v
Abstract
Background: The African swine fever virus (ASFV) is a highly pathogenic double-stranded DNA virus that poses a significant threat to the global swine industry. Although the CD2v protein encoded by ASFV is a key factor in viral immune evasion and pathogenicity, the mechanism underlying its interaction with host proteins remains unclear.
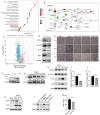
Methods: The aim of this study was to identify a range of potential host proteins that interact with the CD2v protein using the membrane yeast two-hybrid technology.
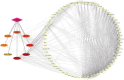
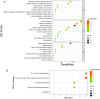
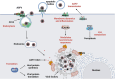
Results: Through subsequent validation experiments and functional analyses, we discovered that these proteins are involved in critical cellular processes such as translational regulation, inflammatory responses, immune signaling, and iron metabolism. Furthermore, interaction network and functional enrichment analyses revealed that ASFV might influence host cell functions through multiple pathways to facilitate viral replication.
Conclusion: This study provides new insights into the pathogenic mechanisms of ASFV and offers valuable clues for identifying antiviral targets.
Keywords: African swine fever virus; CD2v; dual membrane system; interaction network; membrane protein interaction.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Zhu, Li, Hao, Liang, Hu, Sun, Peng, Li, Huang, Zhang, Gong and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

