Altered immunometabolic response to fasting in humans living with obesity
- PMID: 40662191
- PMCID: PMC12256293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112872
Altered immunometabolic response to fasting in humans living with obesity
Abstract
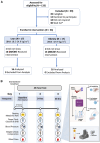
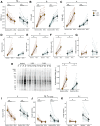
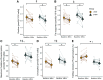
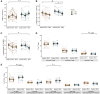
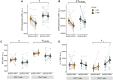
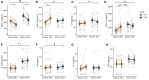
Fasting and ketosis are gaining interest for treating obesity-related immunometabolic dysfunction. We aimed to (1) characterize systemic and T cell immunometabolic responses to a 48-h fast in humans and (2) determine if responses differed between individuals with (O-BMI) and without (L-BMI) obesity (n = 16 per group). Despite similar increases in systemic fat oxidation, increases in blood β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), BHB-amino acid conjugates, and lysine β-hydroxybutyrylation were blunted in obesity. T cells from the L-BMI group upregulated their relative capacity for fat oxidation while the O-BMI group did not. The O-BMI group had a greater proportion of Th17 cells and secreted more interleukin-17 (IL-17), even after fasting. CD8 expression decreased in both groups and CD4 expression only decreased in the L-BMI group. The balance of anti-to pro-inflammatory cytokines increased less in the O-BMI group. Collectively, these findings show that humans living with obesity have a blunted systemic and T cell immunometabolic response to fasting. NCT05886738.
Keywords: human metabolism; immunology.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
J.P.L. is Chief Scientific Officer for the not-for-profit Institute for Personalized Therapeutic Nutrition. J.P.L. holds founder shares in Metabolic Insights Inc., a for-profit company that developed non-invasive metabolic monitoring devices.
Figures

References
-
- Phelps N.H., Singleton R.K., Zhou B., Heap R.A., Mishra A., Bennett J.E., Paciorek C.J., Lhoste V.P., Carrillo-Larco R.M., Stevens G.A., et al. Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: a pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2024;403:1027–1050. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nishimura S., Manabe I., Nagasaki M., Eto K., Yamashita H., Ohsugi M., Otsu M., Hara K., Ueki K., Sugiura S., et al. CD8 + effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat. Med. 2009;15:914–920. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

