Regulatory effects of head acupuncture on the GABAergic system and Wnt7a/β-catenin pathway in post-stroke spasticity rats
- PMID: 40663208
- PMCID: PMC12263488
- DOI: 10.1007/s10735-025-10505-4
Regulatory effects of head acupuncture on the GABAergic system and Wnt7a/β-catenin pathway in post-stroke spasticity rats
Abstract
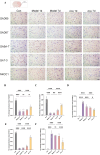
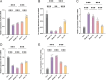
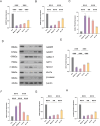
To investigate the regulation of the GABAergic system and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in rats with limb spasticity after stroke by Head Acupuncture therapy and its potential mechanism. A middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model was established by the thread bolus method, and randomly grouped into a blank group, a model group, and a needling group, the latter of which received the intervention of needling at the points of "Hundred Houses" and "Rate Valley" for 30 min a day for 7 consecutive days. The neurological deficits and muscle tone of rats were assessed by Zeo Longa score and modified Ashworth score, and the expression levels of key proteins of the GABAergic system (GAD65, GAD67, GABA-T, GAT-3, NKCC1) and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway were detected by immunohistochemistry, real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR and Western blot and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway key protein expression levels. Head Acupuncture significantly improved the neurological deficit score and muscle tone of rats in the model group, decreased the mRNA and protein expression levels of GABA-T and NKCC1, and significantly up-regulated the expression of GAD65, GAD67, and GAT-3. In addition, acupuncture promoted the expression of Wnt7a and β-catenin, and the effect of 7 days of treatment was better than that of 1 day. Head Acupuncture therapy may exert a therapeutic effect on limb spasticity after stroke by regulating the balance of the GABAergic system and activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This provides a new experimental basis for the application of acupuncture in post-stroke sequelae.Clinical trial number: 2024062814.
Keywords: GABAergic system; Head acupuncture; Limb spasticity; Spasticity rats; Wnt/β-catenin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors consent to publish. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Effect of Jingjin needling on the proliferation and differentiation of skeletal muscle satellite cells in rats with knee osteoarthritis].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Jul 25;50(7):799-807. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20240421. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40691030 Chinese.
-
Three-dimensional kinematic analysis can improve the efficacy of acupoint selection for post-stroke patients with upper limb spastic paresis: A randomized controlled trial.J Integr Med. 2025 Jan;23(1):15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2024.12.004. Epub 2024 Dec 12. J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 39710552 Clinical Trial.
-
[Acupuncture inhibits cuproptosis to prolong the time window of thrombolysis by down-regulating cerebral FDX1 and DLAT in rats with cerebral infarction].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Jul 25;50(7):754-762. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20240274. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40691025 Chinese.
-
[Effectiveness of acupuncture in spasticity of the post-stroke patient. Systematic review].Aten Primaria. 2016 Apr;48(4):226-34. doi: 10.1016/j.aprim.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Aten Primaria. 2016. PMID: 26168934 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
Acupuncture for treating fibromyalgia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD007070. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007070.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashworth B (1964) Preliminary trial of carisoprodol in multiple sclerosis. Practitioner 192:540–542 - PubMed
-
- Bi D, Wen L, Wu Z et al (2020) GABAergic dysfunction in excitatory and inhibitory (E/I) imbalance drives the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 16(9):1312–1329 - PubMed
-
- Chen B, Tao J, Lin Y et al (2015) Electro-acupuncture exerts beneficial effects against cerebral ischemia and promotes the proliferation of neural progenitor cells in the cortical peri-infarct area through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 36(5):1215–1222. 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2334 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

