Pattern recognition in living cells through the lens of machine learning
- PMID: 40664239
- PMCID: PMC12303112
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.240377
Pattern recognition in living cells through the lens of machine learning
Abstract
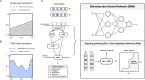
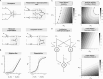
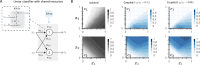
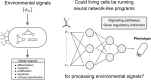
At a coarse level, pattern recognition within cells involves sensing of environmental signals by surface receptors, and activating downstream signalling pathways that ultimately drive a transcriptome response, enabling biological functions such as differentiation, migration, proliferation, apoptosis or cell-type specification. This kind of decision-making process resembles a classification task that, inspired by machine learning concepts, can be understood in terms of a decision boundary: the combination of inputs relative to the classification region defined by this boundary defines context-specific responses. In this report, we contextualize machine learning concepts within a biological framework to explore the structural and functional similarities (and differences) between artificial neural networks, signalling pathways and gene regulatory networks. We take a preliminary look at neural network architectures that may better suit biological classification tasks, explore how learning fits into this paradigm, and address the role of competitive binding in cellular computation. Altogether, we envision a new research direction at the intersection of systems and synthetic biology, advancing our understanding of the inherent computational capacities of signalling pathways and gene regulatory networks.
Keywords: biocomputation; neural networks; pattern recognition; signalling pathways; synthetic biology.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Deciphering Shared Gene Signatures and Immune Infiltration Characteristics Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Preeclampsia by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning.Reprod Sci. 2025 Jun;32(6):1886-1904. doi: 10.1007/s43032-025-01847-1. Epub 2025 May 15. Reprod Sci. 2025. PMID: 40374866
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
A Spectrum of Understanding: A Qualitative Exploration of Autistic Adults' Understandings and Perceptions of Friendship(s).Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):438-450. doi: 10.1089/aut.2023.0051. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018059
-
Advancements in AI for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics: A Comprehensive Review.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2952:87-105. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4690-8_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40553329 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

