Associations between Life's Essential 8 and stroke: findings from NHANES 2005-2018
- PMID: 40664413
- PMCID: PMC12265821
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093362
Associations between Life's Essential 8 and stroke: findings from NHANES 2005-2018
Abstract
Background: Stroke poses a significant financial and medical burden as it is the primary cause of death and disability globally. The identification of modifiable risk factors is crucial in the prevention of stroke. Life's Essential 8 (LE8) is the most recent indicator of cardiovascular health, but its association with stroke is unclear.
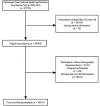
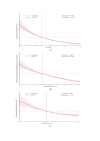
Methods: Using information from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted in 2005-2018, we evaluated the relationship between the LE8 score and the self-reported incidence of stroke in adult US citizens aged 20 years or older on a cross-sectional basis. LE8 scores were classified as being high, moderate or low according to American Heart Association guidelines. The stroke status was ascertained through self-reporting, and the analysis was adjusted for potential confounders. In addition, restricted cubic spline (RCS) analyses were used to further analyse the potential non-linear correlation between the LE8 score and the risk of stroke.
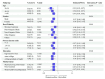
Results: In our study, a total of 24 851 study participants were included, with 943 strokes and a male prevalence of 48.21%. After adjusting for all covariates, the odds of stroke were 2.17 (95% CI: 1.41 to 3.33) and 4.81 (95% CI: 3.07 to 7.56) in those with medium and low LE8 scores compared with those with a high LE8 score, respectively. Both the health behaviour score and the health factor score exhibit a significant association with stroke risk. RCS further confirmed that the association was linear. Finally, subgroup analysis has further confirmed the robustness of the observed associations.
Conclusions: Our observation suggests an important independent negative association between LE8 score and stroke risk. This study demonstrates the utility of LE8 as a public health tool for stroke risk stratification and emphasises the importance of cardiovascular health in stroke prevention.
Keywords: Cardiovascular Disease; Risk Factors; Stroke.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Feigin VL, Owolabi MO, World Stroke Organization–Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group Pragmatic solutions to reduce the global burden of stroke: a World Stroke Organization-Lancet Neurology Commission. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22:1160–206. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00277-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
