DDX39B K63-linked ubiquitination mediated by TRIM28 promotes NSCLC metastasis by enhancing ECAD lysosomal degradation
- PMID: 40664668
- PMCID: PMC12263876
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-025-02305-9
DDX39B K63-linked ubiquitination mediated by TRIM28 promotes NSCLC metastasis by enhancing ECAD lysosomal degradation
Abstract
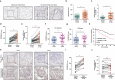
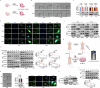
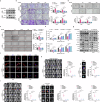
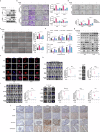
Metastasis is a leading cause of treatment failure and high mortality in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Recently, we demonstrated that DEAD box helicase 39B (DDX39B) was upregulated and activated metabolic reprogramming in colorectal cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. However, the function of DDX39B and the therapeutic potential for targeting DDX39B in NSCLC remain unclear. Herein, we discovered that DDX39B was an independent marker for poor survival in NSCLC patients. Strikingly, DDX39B protein, but not its mRNA, was elevated in clinical metastatic brain lesions and metastatic cell models (in vitro EMT-metastatic and in vivo carotid artery injection-induced brain-metastatic cell model). Mechanistically, DDX39B interacted with E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM28 via Pro322 residue and underwent TRIM28-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination at Lys241, Lys384, and Lys398, leading to DDX39B protein stabilization and upregulation. Subsequently, DDX39B directly bound to ECAD and promoted ECAD lysosomal degradation by recruiting Src and Hakai, which was independent of its RNA helicase activity, followed by activating β-catenin oncogenic signaling and facilitating NSCLC aggressive phenotype. According to structure-based virtual screening, we discovered a clinical antimalarial drug, artesunate, that disrupted the association of DDX39B-TRIM28 complex, resulting in DDX39B degradation and blocking the pro-metastatic effects of DDX39B. Overall, our findings uncover that TRIM28/DDX39B/ECAD axis contributes to NSCLC metastasis and targeting DDX39B degradation by artesunate is an effective and promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of NSCLC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E. & Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA-Cancer J. Clin.72, 7–33 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Yousefi, M. et al. Lung cancer-associated brain metastasis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic options. Cell. Oncol.40, 419–441 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Li, K. et al. ZNF32 induces anoikis resistance through maintaining redox homeostasis and activating Src/FAK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.442, 271–278 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82272892/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82404000/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82103525/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 2023ZYD0044/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2024YFFK0383/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

