Sensitive detection of dengue serotype-4 on lignin-derived graphene nanofibre and manganese oxide composite by DNA-sensing
- PMID: 40664807
- PMCID: PMC12263869
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-10518-9
Sensitive detection of dengue serotype-4 on lignin-derived graphene nanofibre and manganese oxide composite by DNA-sensing
Abstract
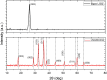
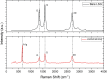
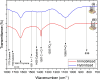
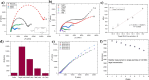
This research addresses the critical challenge of achieving precise DNA detection in complex biological samples by developing a novel, eco-friendly dengue virus serotype 4 biosensor. Utilizing laser-scribed graphene nanofibers derived from sustainable oil palm lignin, a cost-effective alternative to conventional graphene, the biosensor leverages the material's high surface area and conductivity for enhanced DNA immobilization and signal transduction. While lignin-derived graphene's heterogeneous structure poses challenges to electrochemical performance, this study overcomes these limitations by synthesizing laser scribed-graphene nanofibres (LSGNF) decorated with manganese oxide nanoparticles. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy images revealed a highly advantageous three-dimensional, interconnected network of thin, wrinkled sheets forming a porous scaffold, providing efficient electron transport and enhanced molecular interaction. Transmission electron microscopy further confirmed the successful integration of Mn3O4 nanoparticles onto the LSGNF surface. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy corroborated the formation of the LSGNF/Mn3O4 nanocomposite, demonstrating successful material synthesis. A dengue-specific DNA probe was then immobilized onto the nanocomposite surface, and its hybridization with complementary target DNA was evaluated. Successful DNA immobilization and hybridization were confirmed by the detection of phosphorus and nitrogen peaks using FTIR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy revealed the biosensor's high sensitivity, detecting dengue DNA at femtomolar concentrations (10⁻¹⁵ M) with a significant decrease in impedance upon hybridization and a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 3:1, surpassing typical DNA biosensors with SNRs of 1:1 to 2:1. The biosensor exhibited excellent selectivity, optimized between SMM, TMM and NC, stability over an 8-week study, and reproducibility across five repetitive IDEs. This promising advancement in dengue diagnostics offers a faster response, improved sensitivity, and cost-effectiveness for early disease detection and management.
Keywords: Dengue biosensor; Laser-scribed graphene; Manganese oxide nanoparticle; Nanomaterial.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hybrid g-C₃N₄/ZnO nanocomposites for enhanced electrochemical detection of dengue virus serotype 2 (DENV2) NS1 protein biomarker.Mikrochim Acta. 2025 Jun 23;192(7):448. doi: 10.1007/s00604-025-07307-6. Mikrochim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40551020
-
A novel MIP electrochemical sensor based on a CuFe2O4NPs@rGO nanocomposite and its application in breast milk samples for the determination of fipronil.Anal Methods. 2025 Jul 3;17(26):5508-5518. doi: 10.1039/d5ay00911a. Anal Methods. 2025. PMID: 40557723
-
Exploring a green and precise approach based on graphene oxide-cobalt ferrite nanocomposite for detection and quantification of vitamin B9 and antibacterial assessment.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 4;15(1):23964. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09893-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40615669 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

