Developing angiogenesis-related prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic strategies in bladder cancer using deep learning and machine learning
- PMID: 40665008
- PMCID: PMC12263826
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-08945-9
Developing angiogenesis-related prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic strategies in bladder cancer using deep learning and machine learning
Abstract
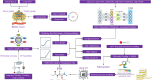
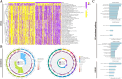
Bladder cancer (BLCA) is a prevalent urological malignancy that exhibits a high degree of tumor heterogeneity and morbidity. Tumor angiogenesis, a vital hallmark of cancer, greatly influences the tumor microenvironment (TME). The emergence of anti-angiogenic drugs has provided a new turning point in cancer treatment. An integrated machine learning system was constructed to build the angiogenesis-related gene signatures (ARGS). ARGS was used to assess TME status in BLCA. Pharmacophore construction was employed to construct pharmacophore features of highly cytotoxic drug payload combinations for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). In addition, we developed a natural compound using artificial intelligence-driven drug design technology. This compound exhibits anti-angiogenic effects in BLCA and serves as a highly cytotoxic drug payload for ADCs. Multi-dimensional machine learning was used to screen biomarkers for evaluating the post-treatment effects of drug therapy in BLCA. The ARGS consists of 12 angiogenesis-related genes associated with prognostic risk in BLCA. The ARGS divides BLCA patients into high-risk and low-risk groups. Significant TME remodeling was identified in the high-risk BLCA cohort and demonstrated a strong association with tumor angiogenesis. Expression levels of key immune checkpoint markers significantly differed between BLCA risk groups. Saikosaponin D (SSD) shows promising potential as a novel ADC drug for anti-angiogenic treatment in BLCA. Multi-dimensional machine learning results indicate that MYH11 is the most likely biomarker for evaluating the post-treatment effects of SSD therapy. SSD may potentially treat tumors by regulating angiogenesis in BLCA. The detection of MYH11 can be used to assess the therapeutic effectiveness of SSD in BLCA.
Keywords: Antibody-drug conjugates; Artificial intelligence-driven drug design; Bladder cancer; Machine learning; Pharmacophore; Protein homology modeling; Saikosaponin D.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: No ethical approval was required for this study. Consent for publication: The published version of the manuscript has been read and approved by all authors. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Conflict of interest: The authors state that this study was conducted without commercial or financial relationships that could be interpreted as potential conflicts of interest. Data sharing and data accessibility: The datasets analyzed during this study are available in the TCGA and GEO databases at https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/ and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ . The collected data used in the research are available from the corresponding author upon enquiry. The illustrations used in the workflow diagrams are from Bioicons ( https://bioicons.com/ ) and are used with permission.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Pathway-based cancer transcriptome deciphers a high-resolution intrinsic heterogeneity within bladder cancer classification.J Transl Med. 2025 Jun 17;23(1):666. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06682-1. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40528211 Free PMC article.
-
Lactylation prognostic signature identifies DHCR7 as a modulator of chemoresistance and immunotherapy efficacy in bladder cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 15;16:1585727. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1585727. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40735323 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine-mediated metabolic immune crosstalk indicates and promotes immunosuppression with anti-PD-1 resistance in bladder cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 24;16:1618439. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1618439. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40630945 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Lopez-Beltran, A., Cookson, M. S., Guercio, B. J. & Cheng, L. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. BMJ384, e076743 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GDMU2023355/Guangdong Medical University Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program
- A2023290/Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- GDMULCJC2024054/The Clinical and Basic Science Innovation Special Program of Guangdong Medical University
- 2022A1515012195/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 2021A05091/Zhanjiang Science and Technology Plan Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

