Hyperglycemia and insulin use in patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxemia allocated to 12 mg vs. 6 mg of dexamethasone: a secondary analysis of the COVID STEROID 2 randomized trial
- PMID: 40665171
- PMCID: PMC12263535
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-025-01512-5
Hyperglycemia and insulin use in patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxemia allocated to 12 mg vs. 6 mg of dexamethasone: a secondary analysis of the COVID STEROID 2 randomized trial
Abstract
Background: While dexamethasone has been shown to improve survival in COVID-19, its dose-response relationship with plasma glucose (PG) levels and insulin requirements is poorly understood. This study investigated the impact of 12 mg (higher dose) versus 6 mg (standard dose) of dexamethasone on hyper- or hypoglycemic events and the use of insulin.
Methods: A secondary analysis of a subpopulation of the COVID STEROID 2 trial. Glycemic outcomes were assessed by time-to-event analysis of a hyperglycemic (two PG measurements ≥ 11.1 mmol/L), severe hyperglycemic (PG > 20 mmol/L), hypoglycemic (< 3.8 mmol/L) event or use of insulin, adjusted for age, diabetes status, hospital site, and mechanical ventilation. PG levels were compared before and after treatment allocation with linear mixed models to estimate changes in average PG levels over time.
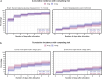
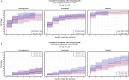
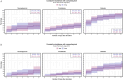
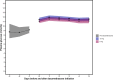
Results: Of 321 participants, 170 were allocated to the higher dose and 151 to the standard dose of dexamethasone. Time to a hyperglycemic event did not differ between groups, whereas severe hyperglycemic events were more frequent in the higher dose group (36%) than in the standard dose group (31%) with an adjusted subdistributional hazard ratio of 1.76 (95% CI [1.22-2.54], p = 0.003). Insulin use and hypoglycemic events did not differ between groups. The higher vs. standard dose group had an average PG increase of 0.5 mmol/L (95% CI [- 0.2 to 1.4], p = 0.149).
Conclusion: Higher vs. standard doses of dexamethasone were associated with a higher incidence of severe hyperglycemia in patients with COVID-19 and severe hypoxemia, but the average increase in PG was similar between groups.
Keywords: Adverse events; COVID-19; COVID-steroid 2 trial; Dexamethasone treatment; Higher and standard dose; Hyperglycemia; Hypoglycemia; Insulin; Secondary analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The COVID STEROID 2 trial was approved by the Scientific Ethics Committee of the Capital Region of Denmark (H-20051056) and registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04509973) and ctri.nic.in (CTRI/2020/10/028731) on August 11th, 2020. The secondary analysis was approved according to Danish Healthcare Law § 46, Sect. 2 by the Capital Region (R-24013197). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: T.B. reports grants from Novo Nordisk Foundation, Lundbeck Foundation, Simonsen Foundation, GSK, and Pfizer; personal fees from GSK, Pfizer, Bavarian Nordic, Gilead, MSD, Janssen, Moderna and Astra Zeneca; outside the submitted work. TPA holds stocks in Novo Nordisk A/S; outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
References
-
- The RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19—preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 2020. 10.1056/NEJMoa2021436.
-
- Umpierrez GE, et al. Hyperglycemia: an independent marker of in-hospital mortality in patients with undiagnosed diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:978–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

