ZSCAN4 functions as a safeguard to maintain centromere integrity during oocyte meiosis
- PMID: 40665375
- PMCID: PMC12261598
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-025-03687-3
ZSCAN4 functions as a safeguard to maintain centromere integrity during oocyte meiosis
Abstract
Background: Centromeres play a vital role in ensuring accurate chromosome segregation during meiosis by serving as the foundation for kinetochore assembly and microtubule attachment. In oocytes, maintaining centromere integrity is particularly critical due to the extended arrest period prior to meiotic resumption. However, the molecular safeguards that preserve centromere structure and function throughout oocyte maturation remain poorly understood.
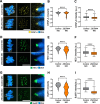
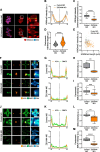
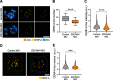
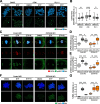
Results: Here, we identify ZSCAN4 as an essential regulator of centromere integrity during mouse oocyte meiosis. ZSCAN4 depletion leads to a marked reduction in key centromeric and kinetochore proteins, including CENP-A, accompanied by aberrant centromere stretching under spindle tension. Mechanistically, ZSCAN4 promotes pericentromeric H3K9me3 enrichment, facilitating proper chromatin compaction and chromosome alignment. Moreover, ZSCAN4 contributes to genomic stability by mediating the chromosomal recruitment of the CIP2A complex in response to DNA damage during meiotic progression.
Conclusions: These findings establish ZSCAN4 as a critical factor in preserving centromere structure and function during oocyte meiosis, with potential implications for female reproductive health and developmental competence.
Keywords: Centromere; Meiosis; Oocytes; SMC family; ZSCAN4.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Animal experiments were performed in strict compliance with institutional guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Sungkyunkwan University (approval ID: SKKUIACUC2023-09–31-1). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Uhlmann F. SMC complexes: from DNA to chromosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17:399–412. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

