CC48 a new CB2R agonist/FAAH inhibitor dual drug blocks gastric cancer progression and overcomes paclitaxel resistance
- PMID: 40665405
- PMCID: PMC12265377
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-025-03476-7
CC48 a new CB2R agonist/FAAH inhibitor dual drug blocks gastric cancer progression and overcomes paclitaxel resistance
Abstract
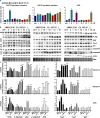
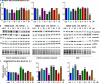
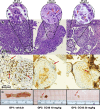
Gastric cancer (GC) has poor survival in advanced stages, with limited treatment options. Paclitaxel (PTX) is commonly used, but resistance often arises, highlighting the need for targeted therapies. Cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2R) is overexpressed in several cancers and its activation has been associated with reduced tumor growth and metastasis. This study evaluated the antitumor activity of selected CB2R agonists with dual activity (CC48 and Fi9) compared to single-target compounds (ASF151), a reference agonist (compound 1), and an antagonist (AM630). The compounds' cytotoxicity was determined in GC lines, including PTX-resistant cells, with different levels of CB2R expression. Firstly, were ported that the addition of CB2R ligands to PTX significantly reduces the actively proliferating cells (Ki67+) even in chemotherapy-resistant GC cells. Concentrations below the IC50 of all compounds were used to minimise toxicity. Activation of Akt/mTORC1 and MAPK cascades were found to be related to antiproliferative activity, which was found to be independent of CB2R expression in the different cell lines. Surprisingly, both agonist and antagonist compounds inhibited cell growth. The interaction of CC48 and the reference compounds 1 and AM630, with P-glycoprotein (P-gp) could explain their greater effectiveness in overcoming PTX resistance. Furthermore, CC48 was particularly effective among the agonists in inducing the expression of key autophagy proteins and activating the apoptotic pathway via caspase 3/7 (p < 0.05). The combination of CC48 with PTX further amplified this effect in both sensitive and resistant cells (p < 0.01). CC48 significantly reduced GC cells migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by modulating the vimentin protein (p < 0.05). In an orthotopic mouse model, CC48 inhibits tumor volume (p < 0.01)and also reduces the number of Ki67 + cells (p < 0.05), without cytotoxic effects. Histological analysis revealed widespread necrosis with inflammatory and apoptotic features, including pyknotic nuclei and fibrotic replacement in CC48-treatedtumors. Moreover, CC48 treatment reduced circulating levels of G-CSF, IL-12 (p40), and eotaxin (p < 0.05), suggesting an immunomodulatory role. In conclusion CC48, a novel multi-target ligand (MTDL), activating CB2R and inhibiting Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH), effectively blocks GC progression modulating the immune response and overcoming PTX resistance.
Keywords: CB2R ligands; Cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R); Gastric cancer treatment; Novel target therapy; Paclitaxel-resistance.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was performed in the Test Facility BIOGEM(S.c.ar.l., Via Camporeale Area P.I.P., Ariano Irpino (AV) Italy) which is authorized to carry out this experimentation by means of the Ministerial Authorization n° 257I2023-PR and authorized for the use of animals for scientific purpose and regulatory research according to the Italian Decree N° 26/2014: authorization N° 08/2023-UT del 23/03/2023. The Test Facility Biogem is GLP certified and the in vivo phase of the study was performed under GLP-like conditions.Any deviation from normality was recorded. In case of death, a necropsy was performed. The animals were managed according to Directive 2010/63/UE regarding the protection of animals used for experimental or other scientific purposes, enforced by the Italian decree n° 26 of March 4, 2014. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



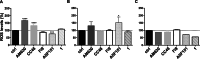





References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. Epub 2021/02/05. - PubMed
-
- Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van Grieken NC, Lordick F. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2020;396(10251):635–48. Epub 2020/08/31. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, et al. Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: a report of the V325 study group. J Clin Oncology: Official J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2006;24(31):4991–7. Epub 2006/11/01. - PubMed
-
- Wilke H, Muro K, Van Cutsem E, Oh SC, Bodoky G, Shimada Y, et al. Ramucirumab plus Paclitaxel versus placebo plus Paclitaxel in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): a double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(11):1224–35. Epub 2014/09/23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

