The Variant rs7665090 Is Associated With Interferon-Beta Response in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
- PMID: 40665510
- PMCID: PMC12263501
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.70227
The Variant rs7665090 Is Associated With Interferon-Beta Response in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
Background: GG homozygosity for the risk gene variant rs7665090 has been reported to enhance nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) activity in T cells from multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. Here, we investigated the association between this polymorphism and the response to different disease-modifying therapies in MS.
Methods: The rs7665090 polymorphism was genotyped in 558 MS patients treated with injectable therapies [IFNβ (n = 213) and glatiramer acetate (n = 55)], oral therapies [dimethylfumarate (n = 97), teriflunomide (n = 41), and fingolimod (n = 37)], and natalizumab (n = 115). Treatment response was assessed after 1 year for injectable therapies using the Rio Score, which considers relapses, EDSS progression, and radiological activity on MRI. For oral therapies and natalizumab, response was evaluated after 2 years based on clinical and radiological disease activity. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression analyses were performed to assess treatment response for each therapy independently.
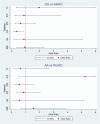
Results: GG homozygosity was associated with a favorable response outcome in patients treated with IFNβ in the multivariable analysis after adjusting for age and EDSS at treatment onset [OR 0.42 (0.18-0.94); p = 0.037]. This finding was restricted to MS patients carrying the GG risk genotype and seemed specific for IFNβ treatment, since the rs7665090 polymorphism did not influence the response to the other MS therapies.
Conclusion: The polymorphism rs7665090 is associated with a favorable response to IFNβ. This study illustrates how genotyping this polymorphism could serve as a useful biomarker in clinical practice to help identify MS patients who are likely to respond favorably to treatment, and encourages further replication in larger cohorts.
Keywords: biomarkers; genetics; interferon; multiple sclerosis; nuclear factor kappa B; treatment response.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

