Rapid Screening of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using MALDI-TOF MS and Machine Learning: A Randomized, Multicenter Study
- PMID: 40665608
- PMCID: PMC12311893
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c01286
Rapid Screening of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Using MALDI-TOF MS and Machine Learning: A Randomized, Multicenter Study
Abstract
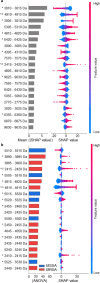
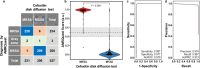
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a major cause of healthcare-associated infections including bacteremia. The rapid detection of MRSA is essential for prompt treatment and improved outcomes. However, traditional MRSA screening and confirmatory tests based on bacterial cultures with antimicrobial susceptibility tests and/or molecular diagnostics are time-consuming (>2 days), labor-intensive, and costly. We report that AMRQuest software, which was developed using logistic regression-based machine learning and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight spectra of S. aureus isolates, can be successfully implemented in clinical microbiology laboratories to screen MRSA and identify bacterial species simultaneously, with the cefoxitin disk diffusion test as a reference. Analytical sensitivity, specificity, percent agreement, and Cohen's kappa values were calculated to determine the accuracy of the AMRQuest software. The minimum sample size of the testing set for statistical analysis was determined considering the local prevalence of MRSA infections. MRSA screening was performed using 537 consecutive S. aureus isolates, including 231 MRSA and 306 methicillin-susceptible S. aureus isolates, from three tertiary-care hospitals. The results from the AMRQuest software were similar to those obtained using the reference method, cefoxitin disk diffusion testing, making it a powerful method for the rapid detection of MRSA prior to traditional antibiotic resistance testing.
Figures
References
-
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust and Government of the United Kingdom, 2016.
-
- Weis C., Cuénod A., Rieck B., Dubuis O., Graf S., Lang C., Oberle M., Brackmann M., So̷gaard K. K., Osthoff M., Borgwardt K., Egli A.. Direct antimicrobial resistance prediction from clinical MALDI-TOF mass spectra using machine learning. Nat. Med. 2022;28:164–174. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01619-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ito T., Katayama Y., Asada K., Mori N., Tsutsumimoto K., Tiensasitorn C., Hiramatsu K.. Structural comparison of three types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec integrated in the chromosome in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus . Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001;45:1323. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.5.1323-1336.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

