Genome-wide identification of LHT gene family in Lonicera macranthoides Hand.-Mazz and their responses to abiotic stresses
- PMID: 40666075
- PMCID: PMC12259443
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1614541
Genome-wide identification of LHT gene family in Lonicera macranthoides Hand.-Mazz and their responses to abiotic stresses
Abstract
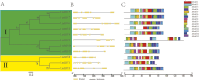
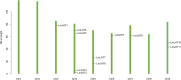
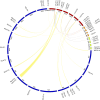
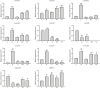
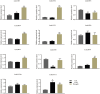
Amino acid transporters (AATs) allow the transport of amino acids and play important roles in the various physiological processes and environmental responses of plants. The lysine and histidine transporter (LHT) subfamily is an important type of AAT. However, a genome-wide overview of the LHT gene family has not been conducted in L. macranthoides Hand.-mazz. In this study, 11 LHT genes were identified in the Lonicera macranthoides genome. To further understand the functions of LmLHT genes, the gene and protein characteristics, transmembrane helices, evolutionary relationships, chromosomal distribution, cis-acting elements of promoters, and expression patterns were systematically analyzed. According to the results, LmLHT genes were divided into two groups based on the phylogenetic analysis. Transmembrane helices of LmLHT proteins ranged from seven to 16. Gene structure and conserved motif analysis revealed that exon-intron structures and motifs were relatively conserved in the LmLHT family. LmLHT genes were distributed on six of the nine chromosomes and had the most collinear gene pairs with NtLHT genes. Additionally, phytohormones, low-temperature, drought-inducibility, defense and stress related cis-acting elements were enriched in the promoters of LmLHT genes. LmLHT genes showed distinct or preferential expression patterns in various tissues, signifying their potential roles in plant growth and development. We also found that some LmLHT genes were responsive to cold and drought stresses, indicating their roles in abiotic stress adaptation. Overall, our results provided comprehensive insight into the LmLHT gene family and will be useful for future functional analyses.
Keywords: AAT; LHT; Lonicera macranthoides Hand.-mazz; abiotic stresses; genome-wide.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Hu, Liang, Chen, Hu, Wu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide characterization of GRAS gene family and their expression profiles under diverse biotic and abiotic stresses in Amorphophallus konjac.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 8;26(1):643. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11777-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40629278 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of the CCT gene family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa) response to abiotic stress.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):593. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11768-7. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40597573 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of COMT Family Genes in Three Vitis Species Reveals Evolutionary Relationships and Functional Divergence.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jul 7;14(13):2079. doi: 10.3390/plants14132079. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648090 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

