Role of glial cells in neurotoxicological effects of alcohol
- PMID: 40666307
- PMCID: PMC12261501
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ant.2025.03.001
Role of glial cells in neurotoxicological effects of alcohol
Abstract
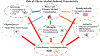
Alcohol (ethanol), presumably consumed as wine as far back as 7000 BC, is most likely the first addictive substance known to man. In modern days, its abuse leading to neurotoxicity and a myriad of organ damages, is of considerable social and medical concern. In the United States alone, approximately 180,000 people die yearly because of alcohol-related accidents and diseases. Given its ubiquitous nature, alcohol may interact with many cellular components. In this chapter, we specifically concentrate on its neurotoxic mechanisms involving glial cells and their role in neuroinflammation. Moreover, exploitation of this knowledge for potential novel interventions in alcohol-induced neurotoxicity are touched upon.
Figures

References
Further reading
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
