This is a preprint.
Genome-wide association meta-regression identifies stem cell lineage orchestration as a key driver of acne risk
- PMID: 40666320
- PMCID: PMC12262744
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.27.25330406
Genome-wide association meta-regression identifies stem cell lineage orchestration as a key driver of acne risk
Abstract
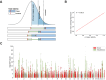
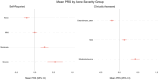
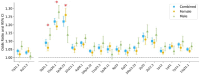
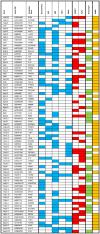
Over 85% of the population experience acne at some point in their lives, with its severity spanning a quantitative spectrum, from mild, transient outbreaks to more persistent, severe forms of the condition. Moderate to severe disease poses a substantial global burden arising from both the physical and psychological impacts of this highly visible condition. The analytical approach taken in this study aimed to address the impact of variation in the dichotomisation of acne case control status, driven by ascertainment and study design, on effect size estimates across independent genetic association studies of acne. Through a fixed intercept meta-regression framework, we combined evidence genome-wide for association with acne across studies in which case-control status had been ascertained in different settings, allowing for different severity threshold definitions. Across a combined sample of 73,997 cases and 1,103,940 controls of European, South Asian and African American ancestry we identify genetic variation at 165 genomic loci that influence acne risk. There is evidence for both shared and ancestry specific components to the genetic susceptibility to acne and for sex differences in the magnitude of effect of risk alleles at three loci. We observe that common genetic variation explains 13.4% of acne heritability on the liability scale. Consistent with the hypothesis that genetic risk primarily operates at the level of individual pilosebaceous units, a polygenic score derived from this case-control study of acne susceptibility is associated with both self-reported and clinically assessed acne severity in adolescence, further strengthening the link between genetic risk and disease severity. Prioritisation of causal genes at the identified acne risk loci, provides genetic validation of the targets of established and emerging acne therapies, including retinoid treatments. The identified acne risk loci are enriched for genes encoding downstream effectors of RXRA signalling, including SOX9 and components of the WNT and p53 pathways. Illustrating that the control of stem cell lineage plasticity and cellular fate are important mechanisms through which genetic variation influences acne susceptibility within the pilosebaceous unit.
Figures
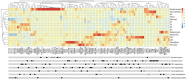
References
-
- Zaenglein A. L. Acne Vulgaris. N. Engl. J. Med. 379, 1343–1352 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Williams H. C., Dellavalle R. P. & Garner S. Acne vulgaris. The Lancet 379, 361–372 (2012).
-
- Vos T. et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet 396, 1204–1222 (2020).
-
- Chen H. et al. Magnitude and temporal trend of acne vulgaris burden in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019: an analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Br. J. Dermatol. 186, 673–683 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Reynolds R. V. et al. Guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 90, 1006.e1–1006.e30 (2024).
Publication types
Grants and funding
- RC2 MH089951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008676/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081802/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008657/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD042157/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR080796/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008679/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008666/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MH068457/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MD007593/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008685/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006379/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008664/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008701/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008684/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- EP-C-15-001/EPA/EPA/United States
- K01 AR075111/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008680/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001875/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 HG008673/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
