The F1F3 recombinant chimera induced higher vaccine efficacy than its independent F1 and F3 components against Leishmania (L.) infantum chagasi mice infection
- PMID: 40666521
- PMCID: PMC12260408
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1598755
The F1F3 recombinant chimera induced higher vaccine efficacy than its independent F1 and F3 components against Leishmania (L.) infantum chagasi mice infection
Abstract
Introduction: Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is a severe human vector-borne CD4-immunosuppressive disease that can be lethal if untreated soon after symptoms arise. No vaccine is available against human VL, and its chemotherapy is highly toxic and requires hospitalization. VL patients show substantially decreased CD4+ total and Leishmania-specific CD4+ T cell counts. Leishmania (L.) donovani nucleoside hydrolase (NH36) is a DNA metabolism enzyme and a conserved marker of the Leishmania genus. It has been considered, among other Leishmania antigens, a vaccine candidate. In mice vaccinated with NH36, protection against VL is mediated by a CD4+ T cell response to the NH36 C-terminal domain (F3), and against cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), by a CD4+ response against F3 and a CD8+ response against the NH36 N-terminal (F1). Vaccination with a recombinant chimera containing the F1 and F3 domains expressed in tandem (F1F3) protected mice against the heterologous CL infection by L. (L.) amazonensis and L. (V.) braziliensis.
Methods: In this investigation, BALB/c mice were immunized with either F1, F3, a mixture of both, or with the F1F3 chimera, plus saponin and challenged with amastigotes of L. (L.) infantum chagasi, the agent of VL in America.
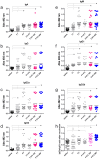
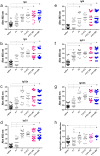
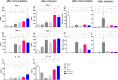
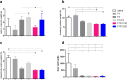
Results: Before and after infection, the F1F3 chimera and the F3 vaccines promoted the highest IgA, IgM, IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG3 antibody responses. The F1F3 chimera promoted the strongest intradermal response against the leishmanial antigen, the highest body weight gain, and the most potent reduction of the spleen and liver relative weights. In addition, the F1F3 chimera vaccine increased the secretion of IFN-γ, and, together with the F3 vaccine, the secretion of TNF-α by splenocytes. The F1F3 chimera and the F1 vaccine also promoted the strongest secretion of IL-10, which was very low in mice immunized with F3. Thus, the IFN-γ/IL-10 and TNF-α/IL-10 ratios, characteristic of a Th1 response, were increased in mice vaccinated with F3. The F1F3 chimera and the F3 vaccine reduced the parasite load in the liver.
Discussion: The F1F3 chimera, as described for the heterologous CL infections, also optimizes protection against the homologous visceral leishmaniasis infection by L. (L.) infantum chagasi, by a Th1 contribution from the F3 peptide and a regulatory response from the F1 peptide. Expression of the F1 and F3 domains in tandem induced higher efficacy than the simple mixture of the F1 and F3 domains.
Keywords: F1F3 recombinant chimera; Leishmania (L.) infantum chagasi; mixed or T-cell regulatory response; nucleoside hydrolase NH36; visceral leishmaniasis.
Copyright © 2025 Gomes, Fonseca-Ribeiro, Alves-Silva and Palatnik-de-Sousa.
Conflict of interest statement
CP-d-S declares a conflict of interest. The Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil have filed a patent application about the results of this research PI1015788-3. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The F1F3 Recombinant Chimera of Leishmania donovani-Nucleoside Hydrolase (NH36) and Its Epitopes Induce Cross-Protection Against Leishmania (V.) braziliensis Infection in Mice.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 9;10:724. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00724. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31024556 Free PMC article.
-
NH36 and F3 Antigen-Primed Dendritic Cells Show Preserved Migrating Capabilities and CCR7 Expression and F3 Is Effective in Immunotherapy of Visceral Leishmaniasis.Front Immunol. 2018 May 7;9:967. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00967. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29867949 Free PMC article.
-
A Chimera Containing CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Epitopes of the Leishmania donovani Nucleoside Hydrolase (NH36) Optimizes Cross-Protection against Leishmania amazonesis Infection.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 23;8:100. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00100. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28280494 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleoside Hydrolase NH 36: A Vital Enzyme for the Leishmania Genus in the Development of T-Cell Epitope Cross-Protective Vaccines.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 16;10:813. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00813. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31040850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for Old World cutaneous leishmaniasis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 1;12(12):CD005067. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005067.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29192424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leishmaniasis. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (Accessed February 25, 2025).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

