Therapeutic mechanisms of polysaccharides in the management of rheumatoid arthritis: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 40666523
- PMCID: PMC12259611
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1608909
Therapeutic mechanisms of polysaccharides in the management of rheumatoid arthritis: a comprehensive review
Abstract
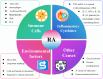
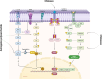
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by synovial inflammation and destruction of articular cartilage and bone, which seriously affects patients' quality of life. In recent years, with the in-depth research on natural medicines, the application of polysaccharides in the treatment of RA has gradually gained attention due to their unique bioactive components and diverse pharmacological effects. Polysaccharides were reported to exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and protective effects on cartilage and bone tissues. This review briefly introduces RA, its etiology and pathogenesis, and the different sources and structures of polysaccharides. It focuses on the mechanisms of polysaccharides in the alleviation of RA, mainly through the modulation of immune cell function, inhibition of inflammation, regulation of gut microbiota, promotion of bone formation and repair, and influence on related pathways. The aim of this review is to summarize the polysaccharides and their mechanisms of action in the alleviation of RA, with a view to providing new ideas for the clinical treatment of RA.
Keywords: cytokines; immune cells; mechanism; polysaccharides; rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Kong, Wang, Yang, Yan and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of the intestinal flora-immunity axis in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis-mechanisms regulating short-chain fatty acids and Th17/Treg homeostasis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 21;52(1):617. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10714-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40544212 Review.
-
The immunomodulatory of interleukin-33 in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review.Clin Immunol. 2024 Aug;265:110264. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2024.110264. Epub 2024 May 31. Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38825072
-
The roles of polysaccharides in rheumatoid arthritis treatment: A review focusing on the sources, structures and their related mechanism.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Sep;321(Pt 2):146377. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.146377. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40738445 Review.
-
Extraction of anthocyanins from purple sweet potato: evaluation of anti-inflammatory effects in a rheumatoid arthritis animal model, mechanistic studies on inflammatory cells, and development of exosome-based delivery for enhanced targeting.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 9;16:1559874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1559874. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40552287 Free PMC article.
-
Balneotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis-a systematic review.Int J Biometeorol. 2016 Aug;60(8):1287-301. doi: 10.1007/s00484-015-1108-5. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Int J Biometeorol. 2016. PMID: 26607275
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

