This is a preprint.
Outer membrane vesicles from Bacteroides fragilis contain coding and non-coding small RNA species that modulate inflammatory signaling in intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 40666935
- PMCID: PMC12262621
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.25.661399
Outer membrane vesicles from Bacteroides fragilis contain coding and non-coding small RNA species that modulate inflammatory signaling in intestinal epithelial cells
Update in
-
Outer Membrane Vesicles From Bacteroides fragilis Contain Coding and Non-Coding Small RNA Species That Modulate Inflammatory Signalling in Intestinal Epithelial Cells.J Extracell Biol. 2025 Oct 21;4(10):e70086. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70086. eCollection 2025 Oct. J Extracell Biol. 2025. PMID: 41127052 Free PMC article.
Abstract
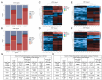
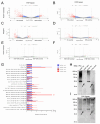
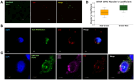
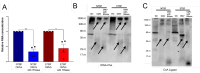
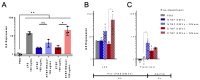
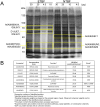
Alterations to the community structure and function of the microbiome are associated with changes to host physiology, including immune responses. However, the contribution of microbe-derived RNAs carried by outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) to host immune responses remain unclear. This study investigated the role of OMVs and OMV-associated small RNA (sRNA) species from pathogenic and commensal Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF and NTBF respectively) in eliciting different immune responses from intestinal epithelial cells. To distinguish the differences in the sRNA profiles of the two strains and their OMVs, RNA-seq, qRT-PCR, and northern blotting were conducted to identify enrichment of discrete sRNA species in OMVs, which were also differentially expressed between the two strains. Specifically, both coding and non-coding RNAs were enriched in OMVs from NTBF and ETBF, with BF9343_RS22680 and BF9343_RS17870 being significantly enriched in ETBF OMVs compared to NTBF. To understand the effects of OMVs on pattern recognition receptors, reporter cells of Toll-like receptor (TLR) activation were treated with OMVs, demonstrating activation of TLRs 2, 3, and 7. Treatment of Caco-2 and HT29-MTX cells with OMVs demonstrated increased expression of IL-8. Surprisingly, we discovered that degradation of RNase-accessible RNAs within ETBF OMVs, but not NTBF OMVs, resulted in vesicles with enhanced capacity to stimulate IL-8 expression, indicating that these extravesicular RNAs exert an immunosuppressive effect. This suggests a dual role for OMV-associated RNAs in modulating host immune responses, with implications for both bacterial pathogenesis and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Bacteroides fragilis; outer membrane vesicles; small RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest Statement The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cancer of the Colon and Rectum - Cancer Stat Facts, <https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html> (
-
- Colorectal Cancer, <https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/colorectal-cancer/> (
-
- Wanders LK, D. E., Pullens B, Bassett P, Travis SPL, East JE. Cancer risk after resection of polypoid dysplasia in patients with longstanding ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 12, 756–764 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
