This is a preprint.
Inhibition of nonsense-mediated decay in TDP-43 deficient neurons reveals novel cryptic exons
- PMID: 40667039
- PMCID: PMC12262666
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.28.661837
Inhibition of nonsense-mediated decay in TDP-43 deficient neurons reveals novel cryptic exons
Abstract
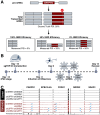
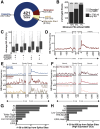
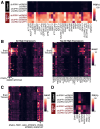
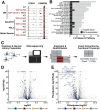
TAR DNA-binding protein 43 kDa (TDP-43) is an essential splicing repressor whose loss of function underlies the pathophysiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (ALS-FTD). Nuclear clearance of TDP-43 disrupts its function and leads to the inclusion of aberrant cryptic exons. These cryptic exons frequently introduce premature termination codons resulting in the degradation of affected transcripts through nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). Conventional RNA sequencing approaches thus may fail to detect cryptic exons that are efficiently degraded by NMD, precluding identification of potential therapeutic targets. We generated a comprehensive set of neuronal targets of TDP-43 in human iPSC-derived i3Neurons (i3N) by combining TDP-43 knockdown with inhibition of multiple factors essential for NMD, revealing novel cryptic targets. We then restored expression of selected NMD targets in TDP-43 deficient i3Ns and determined which genes improved neuronal viability. Our findings highlight the role of NMD in masking cryptic splicing events and identify novel potential therapeutic targets for TDP-43-related neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures
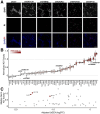
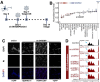
References
-
- Neumann M. et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Science 314, 130–133 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Arai T. et al. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602–611 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
