This is a preprint.
Projection-Specific Intersectional Optogenetics for Precise Excitation and Inhibition in the Marmoset Brain
- PMID: 40667064
- PMCID: PMC12262514
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.18.660378
Projection-Specific Intersectional Optogenetics for Precise Excitation and Inhibition in the Marmoset Brain
Abstract
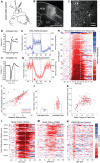
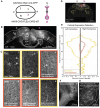
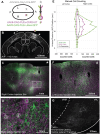
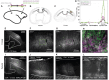
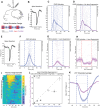
The primate cerebral cortex relies on long-range connections to integrate information across spatially distributed and functionally specialized areas, yet tools for selectively modulating these pathways remain limited. Here, we present an optimized intersectional viral and optogenetic strategy for precisely exciting and inhibiting projection-specific neurons in the common marmoset. Building on a mouse-to-marmoset pipeline, we first validated that optogenetic activation of inhibitory neurons (via AAV9-Dlx-ChR2) enables robust local cortical inhibition. We then combined retrograde delivery of Cre-recombinase (AAVretro-Cre) with locally injected Cre-dependent vectors encoding excitatory or inhibitory opsins (AAV8-FLEx-ChR2 or Jaws) to achieve directionally selective expression in callosal and frontoparietal pathways. Dual-opsin co-expression enabled precise stimulation or suppression of projection neurons in vivo with minimal off-target labeling. These results establish a scalable framework for projection-specific optogenetic interrogation of distributed circuits in primates, expanding the experimental toolkit for causal studies of higher-order brain function with enhanced anatomical precision and functional specificity.
Keywords: Cre recombinase; Dlx-enhancer; Intersectional optogenetics; adeno-associated virus; excitation and inhibition; laminar recording; marmosets; projection-specific; retrograde labeling.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
