This is a preprint.
Cetuximab increases LGR5 expression and augments LGR5-targeting antibody-drug conjugate efficacy in patient-derived colorectal cancer models
- PMID: 40667242
- PMCID: PMC12262463
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.06.18.660406
Cetuximab increases LGR5 expression and augments LGR5-targeting antibody-drug conjugate efficacy in patient-derived colorectal cancer models
Update in
-
Cetuximab increases LGR5 expression and augments LGR5-targeting antibody-drug conjugate efficacy in patient-derived colorectal cancer models.Cell Rep Med. 2025 Oct 21;6(10):102363. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102363. Epub 2025 Sep 18. Cell Rep Med. 2025. PMID: 40972582 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains the second-leading cause of cancer-associated deaths, indicating an urgent need for improved therapeutic options. We previously generated antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting the cancer stem-like cell marker leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (LGR5). However, tumor relapse due to LGR5 downregulation and suboptimal payload selection warranted strategies to improve ADC efficacy. Here we report cetuximab, an EGFR-targeting monoclonal antibody indicated for RAS WJ metastatic CRC, augments LGR5 expression independent of RAS/PIK3CA mutation status and promotes EGFR-LGR5 interactions. Furthermore, we describe the development of LGR5 ADCs incorporating a camptothecin-derived payload that is well-tolerated and significantly inhibits tumor growth. Importantly, cetuximab in combination with LGR5 ADCs results in enhanced tumor inhibition or regression versus single-agent treatment and extends survival in RAS MUT patient-derived xenografts. These findings support growing evidence that ADC combination therapies may be more effective than monotherapies and suggests a broader clinical use for cetuximab in treating RAS MUT CRC.
Keywords: Antibody-drug conjugate; EGFR; LGR5; cetuximab; colorectal cancer; combination treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS K.S.C serves on an advisory board for Merus, NV.
Figures
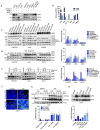
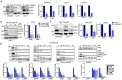
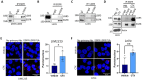

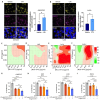

References
-
- Liu W., Zhang J., Gan X., Shen F., Yang X., Du N., Xia D., Liu L., Qiao L., Pan J., et al. (2018). LGR5 promotes epithelial ovarian cancer proliferation, metastasis, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition through the Notch1 signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 7, 3132–3142. 10.1002/cam4.1485. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
