Correlation and predictive modeling of serum exosomal miRNAs and serological biomarkers for lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer
- PMID: 40667557
- PMCID: PMC12256415
- DOI: 10.62347/AOJE4206
Correlation and predictive modeling of serum exosomal miRNAs and serological biomarkers for lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the predictive potential of serum exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) and traditional serological biomarkers for lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer and to assess their applicability in clinical practice.
Methods: This retrospective study included 845 gastric cancer patients treated between January 2020 and December 2023, as the training cohort. Patients were stratified into lymph node-positive (n = 231) and lymph node-negative (n = 614) groups based on postoperative pathological evaluation. Serum exosomal miRNAs and conventional serological biomarkers were quantified and compared between groups. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify independent predictors. Model performance was validated using an independent test cohort comprising 277 patients (74 lymph node-positive, 203 lymph node-negative).
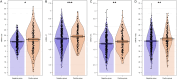
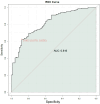
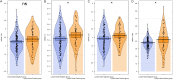
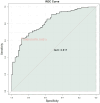
Results: Patients with lymph node metastasis exhibited significantly elevated expression of miR-21, miR-20a, miR-27a, and miR-106a. Serological markers that were significantly higher in the lymph node positive group included carbohydrate antigen 724, carcinoembryonic antigen, hepatocyte growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, interleukin-6, and circulating cell-free DNA (all P < 0.05). A combined predictive model integrating both miRNA and serological data demonstrated strong diagnostic performance, with an area under the curve of 0.816 in the training cohort and 0.817 in the validation cohort.
Conclusion: Serum exosomal miRNAs and serological biomarkers are significantly associated with lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; cancer prognosis; lymph node metastasis; prediction model; serological biomarkers; serum exosome miRNA.
AJCR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction of a prediction model for peripheral lymph node metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer based on enhanced CT texture features.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jul 7;23(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03928-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40624517 Free PMC article.
-
The levels of plasma MiR-9 and MiR-106a are associated with the development of peritoneal carcinomatosis in patients with gastric cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1090. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14427-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597099 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) for the preoperative locoregional staging of primary gastric cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 6;2015(2):CD009944. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009944.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25914908 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a Log odds of negative lymph nodes/T stage ratio-based prognostic model for gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 3;15:1554270. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1554270. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40530015 Free PMC article.
-
Association between HER-2 and Lymph Node Metastasis in Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Oncology. 2025 Jun 12:1-12. doi: 10.1159/000546630. Online ahead of print. Oncology. 2025. PMID: 40505645
References
-
- Nishimuni M, Claro LCL, Braghiroli MIF. Advancements and challenges in gastric cancer: epidemiology, biomarkers, and therapeutic strategies. Surgical and Experimental Pathology. 2024;7:19.
-
- Cai F, Dong Y, Wang P, Zhang L, Yang Y, Liu Y, Wang X, Zhang R, Liang H, Sun Y, Deng J. Risk assessment of lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer: establishment and validation of a seven-point scoring model. Surgery. 2022;171:1273–1280. - PubMed
-
- Yu M, Zhu L, Dong G, Chen J, Ruan B, Liu Y, Yi S, Meng Z, Chen G, Xu W, Huang J, Han F. Spatiotemporal mapping of lymphatic metastases in gastric cancer using tumor-trackable and enzyme-activatable near-infrared fluorescent nanoprobes. ACS Nano. 2024;18:35490–35506. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
