Identification of β4GALNT2 as an anti-hPIV3 factor through genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library screening
- PMID: 40667754
- PMCID: PMC12269090
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2529895
Identification of β4GALNT2 as an anti-hPIV3 factor through genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library screening
Abstract
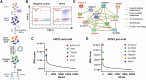
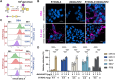
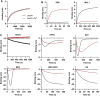
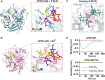
Human respirovirus 3 (also known as human parainfluenza virus 3; hPIV3) is a major cause of severe acute respiratory infections in vulnerable populations. Here we conducted a genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library screen to identify key host factors for hPIV3 infection. In addition to identifying several host proteins involved in glycosylation as proviral factors, we identified β-1,4-N-Acetyl-Galactosaminyltransferase 2 (β4GALNT2) as a potent restriction factor. Further investigation demonstrated that the addition of a GalNAc residue to α2-3-sialylated glycans by β4GALNT2, resulting in the Sda glycotope, disrupted the interaction between the viral hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) attachment protein and sialoglycan receptors. Specifically, the additional GalNAc residue interfered with the interaction of residue W371 in HN with sub-terminal glycan moieties. β4GALNT2-mediated Sda epitope expression also negatively affected infection by other respiroviruses, with the strongest effect being observed for hPIV3.
Keywords: B4GALNT2; CRISPR/Cas9; Paramyxovirus; hPIV3; sialic acid; virus entry.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
