Clinical Trial: Association Between Early Disease Clearance and Long-Term Outcomes-4-Year Results From the Phase 3 UNIFI Study of Ustekinumab in Ulcerative Colitis
- PMID: 40668079
- PMCID: PMC12343057
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.70264
Clinical Trial: Association Between Early Disease Clearance and Long-Term Outcomes-4-Year Results From the Phase 3 UNIFI Study of Ustekinumab in Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
Background: Achievement of disease clearance (simultaneous symptomatic remission and histo-endoscopic mucosal improvement [HEMI]) following induction therapy may lead to better long-term outcomes in ulcerative colitis (UC).
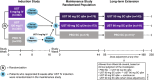
Aim: To evaluate disease clearance in the phase 3 UNIFI program and its association with long-term outcomes.
Methods: UNIFI comprised randomised, placebo-controlled induction and maintenance studies and a long-term extension, which evaluated intravenous ustekinumab induction (130 mg or ~6 mg/kg) and subcutaneous ustekinumab maintenance therapy (90 mg every 8 or 12 weeks) through 4 years in patients with UC.
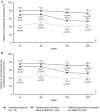
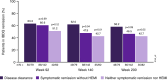
Results: Disease clearance was achieved by 5.9%, 15.2% and 15.1% of patients 8 weeks after placebo or ustekinumab 130 mg or ~6 mg/kg induction, respectively. Among ustekinumab induction responders randomised to ustekinumab maintenance therapy who did or did not achieve disease clearance 8 weeks after induction, 63.6% and 35.2% (nominal p < 0.001), respectively, achieved clinical remission (Mayo score ≤ 2, no individual subscore > 1) at Week 44. Among ustekinumab induction responders randomised to ustekinumab maintenance therapy who achieved disease clearance, symptomatic remission without HEMI, or neither symptomatic remission nor HEMI 8 weeks after induction, 73.4%, 53.5% (nominal p = 0.002) and 45.1% (nominal p < 0.001), respectively, achieved symptomatic remission (Mayo stool frequency subscore 0/1, rectal bleeding subscore 0) and 58.2%, 46.5% (nominal p = 0.09) and 42.7% (nominal p = 0.05), respectively, achieved Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire remission (score ≥ 170) at Week 200.
Conclusions: Patients who achieved disease clearance 8 weeks after ustekinumab induction were more likely to be in long-term clinical, symptomatic and quality of life remission with ustekinumab maintenance treatment than patients who did not.
Trial registration: NCT02407236.
Keywords: disease clearance; ulcerative colitis; ustekinumab.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Silvio Danese reports consultancy fees from AbbVie, Alimentiv, Allergan, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Athos, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Enthera, Ferring, Gilead, Hospira, Inotrem, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Mundipharma, Mylan, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, Sublimity, Takeda, TiGenix, UCB, and Vifor; and reports lecture fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Ferring, Gilead, Johnson & Johnson, Mylan, Pfizer, and Takeda. Rupert W. Leong reports advisory board fees from AbbVie, Aspen, BMS, Celgene, Celltrion, Chiesi, Ferring, Glutagen, Hospira, Johnson & Johnson, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus Biosciences, and Takeda and research grants from Celltrion, Shire, Johnson & Johnson, Takeda, Joanna Tiddy grant from University of Sydney, McCusker Charitable Trust, Gastroenterological Society of Australia, NHMRC, Gutsy Group, and Pfizer. Bruce E. Sands reports non‐financial support from Johnson & Johnson during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Adiso Therapeutics, Agomab, Alimentiv, Amgen, AnaptysBio, Biolojic Design, Biora Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ensho Therapeutics, Enthera, Enveda Biosciences, Equilium, Evommune, Ferring, Fzata, Galapagos, Genetech, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, GossamerBio, Imhotex, Index Pharmaceuticals, Innovation Pharmaceuticals, Kaleido, Kallyope, Microba, Microbiotica, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Mobius Care, Morphic Therapeutics, MRM Health, Nexus Therapeutics, Immunyx Therapeutics, Nimbus Discovery, Odyssey Therapeutics, Palisade Bio, Progenity, Prometheus Laboratories, Protagonist Therapeutics, Q32 Bio, Rasayana Therapeutics, Recludix Therapeutics, Reistone Biotherapeutics, Sorriso Pharmaceuticals, Spyre Therapeutics, Surrozen, Target RWE, Teva, Theravance Biopharma, TLL Pharmaceutical, TR1X, and Union Therapeutics; personal fees and non‐financial support from AbbVie, Abivax, AstraZeneca, Celltrion, Johnson & Johnson, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Prometheus Biosciences, and Takeda; and grants, personal fees, and non‐financial support from Bristol Myers Squibb and Johnson & Johnson; and stock, stock options, personal fees, and non‐financial support from Ventyx Biosciences, all outside of the submitted work. Tony Ma and Colleen Marano report employment with Johnson & Johnson, and Colleen Marano reports Johnson & Johnson stock ownership. Laurent Peyrin‐Biroulet reports grants or contracts from Celltrion, Fresenius Kabi, Medac, MSD, and Takeda; consulting for AbbVie, Abivax, Adacyte, Alfasigma, Alimentiv, Amgen, Applied Molecular Transport, Arena, Banook, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Cytoki Pharma, Enthera, Ferring, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, IAG Image Analysis, Index Pharmaceuticals, Inotrem, Iterative Health, Johnson & Johnson, LifeMine, Lilly, Medac, Mopac, Morphic, MSD, Nordic Pharma, Novartis, Oncodesign, Precision Medicine, ONO Pharma, OSE Immunotherapeutics, Par' Immune, Pfizer, Prometheus, Roche, Roivant, Samsung, Sandoz, Sanofi, Sorriso, Spyre, Takeda, Teva, ThirtyfiveBio, Tillots, Vectivbio, Vedanta, and Ventyx; lecture fees from AbbVie, Alfasigma, Amgen, Arena, Biogen, Celltrion, Ferring, Galapagos, Genentech, Gilead, Iterative Health, Johnson & Johnson, Lilly, Medac MSD, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Sandoz, Takeda, and Tillots; and travel support from Abbvie, Alfasigma, Amgen, Arena, Celltrion, Ferring, Galapagos, Genentech, Gilead, Johnson & Johnson, Lilly, Medac, Morphic, MSD, Pfizer, Sandoz, and Takeda.
Figures



References
-
- Danese S. and Fiocchi C., “Ulcerative Colitis,” New England Journal of Medicine 365 (2011): 1713–1725. - PubMed
-
- Turner D., Ricciuto A., Lewis A., et al., “STRIDE‐II: An Update on the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) Initiative of the International Organization for the Study of IBD (IOIBD): Determining Therapeutic Goals for Treat‐to‐Target Strategies in IBD,” Gastroenterology 160 (2021): 1570–1583. - PubMed
-
- Shah S. C., Colombel J. F., Sands B. E., and Narula N., “Mucosal Healing Is Associated With Improved Long‐Term Outcomes of Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis,” Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 14 (2016): 1245–1255.e8. - PubMed
-
- Colombel J. F., Rutgeerts P., Reinisch W., et al., “Early Mucosal Healing With Infliximab Is Associated With Improved Long‐Term Clinical Outcomes in Ulcerative Colitis,” Gastroenterology 141 (2011): 1194–1201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
