Charcot-Marie-Tooth-like presentation in giant axonal neuropathy: clinical variability and prevalence in a large Japanese case series
- PMID: 40668264
- PMCID: PMC12267338
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-025-13243-5
Charcot-Marie-Tooth-like presentation in giant axonal neuropathy: clinical variability and prevalence in a large Japanese case series
Abstract
Background: Giant axonal neuropathy 1 (GAN) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder with autosomal recessive inheritance and significant phenotypic heterogeneity, ranging from milder presentations resembling Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) to classical presentations involving central and peripheral nervous systems. We investigated the genetic and clinical spectrum of GAN in Japanese patients with inherited peripheral neuropathies (IPNs).
Methods: We conducted genetic screening of 3315 Japanese patients diagnosed with IPNs between 2007 and 2023 using targeted next-generation or whole-exome sequencing. Variant pathogenicity, clinical features, and neurophysiological and neuroimaging findings were reviewed.
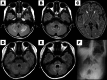
Results: We identified seven biallelic GAN variants in five patients from four unrelated families, including one homozygous and three compound heterozygous genotypes. Two novel pathogenic variants were identified: c.922G > T (p.Glu308*) and c.456dup (p.Ala153Cysfs*27). Two families exhibited the classical phenotype, whereas the other two exhibited a CMT-like phenotype. Mean onset age was 4.4 years (range 1.5-8), and gait disturbance was the initial symptom. The most common findings included distal weakness (n = 5), sensory impairment (n = 4), scoliosis (n = 3), autonomic dysfunction (n = 2). Neurophysiologically, all patients had sensorimotor axonal polyneuropathy. One patient with mild phenotype maintained a CMT-like state without systemic involvement until the age of 43 years and was still alive at 72, representing the longest documented survival in GAN.
Conclusion: This study expands the genetic and phenotypic spectrum of GAN by identifying novel variants and a long-term survivor. These findings underscore the importance of systematic genetic screening for GAN in pediatric-onset CMT, even in the absence of classical features.
Keywords: Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease; Giant axonal neuropathy; Gigaxonin; Inherited peripheral neuropathy; Next-generation sequencing; Phenotypic heterogeneity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study received approval from the institutional review board of Kagoshima University (Application ID: 490). All participants provided their informed consent for their involvement in this study. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

