Mechanistic insights into the anti-aging effects of Crocus sativus in a D-Gal-induced in vitro neural senescence model
- PMID: 40668823
- PMCID: PMC12266386
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320572
Mechanistic insights into the anti-aging effects of Crocus sativus in a D-Gal-induced in vitro neural senescence model
Abstract
Background: The increasing number of elderly individuals has made age-related disorders a significant health concern. Aging is a natural, progressive and gradual phenomenon that leads to irreversible modifications in all molecules, cells, tissues and organs of an organism. Brain senescence is associated with increased risk of developing various neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and stroke. Therefore, finding effective strategies to counteract or delay brain senescence is of great importance for improving the quality of life and health span of the elderly population. Previous studies demonstrated that D-galactose is an appropriate agent to induce aging effects in in vivo and in vitro models.
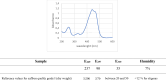
Purpose: In the present study, we evaluated anti-aging effects of a local Saffron extract (SE from Central Italy) on D-GAL-induced aging model in vitro. Based on promising preliminary results, future studies will focus on testing this specific Crocus sativus stigma preparation in animal models of aging.
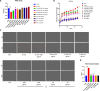
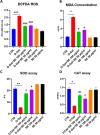
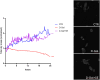
Methods: The potential anti-aging effect was evaluated using assessment of cell proliferation, live-cell cytotoxicity, Beta-Galactosidase (β-GAL), lipid peroxidation, intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. Additionally, the effects of SE pretreatment were examined on cell cycle and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Additionally, we employed a novel approach to analyze deeper changes upon saffron extract treatment, which is label-free holotomography.
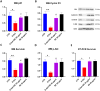
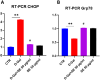
Results: Overall, our findings suggested that pretreatment with SE was protective against D-GAL-induced senescence, by counteracting oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress and proteins that regulate cell death.
Conclusion: We obtained interesting results since pre-treatment with SE ameliorated overall condition, and for the first time we observed the strong anti-aging effect of SE not only in term of morphology, but also dynamics and total dry mass of cells. Overall, our work introduces a novel and promising approach to counteract or delay brain senescence, potentially improving the quality of life and health span of the elderly population.
Copyright: © 2025 Castelli et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic effects of PDGF-AB/BB against cellular senescence in human intervertebral disc.Elife. 2025 Jul 16;13:RP103073. doi: 10.7554/eLife.103073. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40668091 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced senescence in human lung fibroblasts.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):L126-L139. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00264.2023. Epub 2024 May 21. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38771153 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

