Changes in enzyme activity and microbial community of rhizosphere soil under continuously monocultured Passiflora edulis treatment
- PMID: 40668837
- PMCID: PMC12266385
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328363
Changes in enzyme activity and microbial community of rhizosphere soil under continuously monocultured Passiflora edulis treatment
Abstract
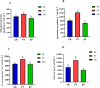
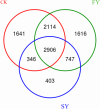
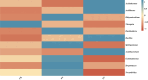
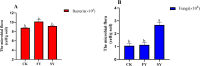
In response to the severe continuous cropping obstacles encountered during the cultivation of passion fruit, which leads to significant declines in yield and quality, as well as rampant pests and diseases, it is particularly important to explore strategies for mitigating these obstacles. The present study used the rhizosphere soil samples from one-year-old (FY, first-year cropping) and two-year-old (SY, second-year cropping) "Golden Passion Fruit" plants, along with soil from uncropped land (CK) as a control and the techniques such as high-throughput sequencing, qRT-PCR, and HPLC-MS to analyze the main physicochemical properties, phenolic acid content, and microbial community changes in the rhizosphere soil of passion fruit under different continuous cropping durations, the results indicated that the contents of total nitrogen, total phosphorus, available nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, and organic matter in FY soil were significantly higher than those in SY soil, and the pH value of the FY soil was also significantly higher than that of SY soil. Additionally, compared with FY soil, the activities of polyphenol oxidase, peroxidase, urease, and invertase in SY soil were significantly reduced by 18.0%, 43.6%, 19.8%, and 45.5%, respectively. HPLC analysis revealed that the concentrations of syringic acid, vanillin, benzoic acid, and ferulic acid in the SY soil were significantly increased by 18.0%, 21.9%, 24.4%, and 21.1%, respectively, compared to those in the FY soil. qRT-PCR analysis showed that as the duration of continuous cropping increased, the total number of bacteria in the rhizosphere soil of passion fruit decreased by 9.37%, while the total number of fungi increased by 57.8%. High-throughput sequencing results demonstrated that at the genus level, the relative abundances of Acidothermus, Acidibacter, Bacillus, and Acidobacterium were significantly increased by38.0%, 56.3%, 34.3%, 77.3%. whereas the relative abundances of Rhizomicrobium, Nitrospira, Burkholderia, Sphingomonas, Gemmatimonas, Streptomyces, and Nocardioides were significantly lower 45.2%,59.3%,50.6%,89.1%,74.5%,82.7% in the SY soil, relative to those in the FY soil. In summary, as the duration of continuous cropping increases, the soil fertility, enzyme activity, pH value, and beneficial microbial content in the rhizosphere of passion fruit decrease significantly, while the contents of phenolic acids and pathogenic microorganisms increase significantly. The findings of this study provide a theoretical basis for further elucidating the formation mechanism and mitigation strategies of continuous cropping obstacles in passion fruit.
Copyright: © 2025 Lin et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Passion fruit plants alter the soil microbial community with continuous cropping and improve plant disease resistance by recruiting beneficial microorganisms.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 21;18(2):e0281854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281854. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36809377 Free PMC article.
-
Responses of rhizosphere bacterial communities with different niche breadths to liquid fertilizer produced from Fuji apple wastes during planting process.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0206824. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02068-24. Epub 2025 May 30. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40445252 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Rhizosphere Soil Microorganisms and Metabolites during the Cultivation of Fritillaria cirrhosa.Biology (Basel). 2024 May 11;13(5):334. doi: 10.3390/biology13050334. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38785816 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
References
-
- Zhang L, Peng X, Cai GJ, Zhang SJ, Wu YH, Li AD. Comprehensive evaluation and analysis of passion fruit in different frame modes. Sci Technol Food Ind. 2021:33–40. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021010027 - DOI
-
- Chen LS, Zhou HY, Weng PY, Fan K, Li ZW, Lin WW. Analysis on the changes of fungal community in rhizosphere soil of Passiflora edulia by continuous cropping of perennial roots based on ITS sequences. Fujian Agric Sci Technol. 2021;52:16–21. doi: 10.13651/j.cnki.fjnykj.2021.05.004 - DOI
-
- Asadu CLA, Dixon AGO. Soil nutrient and cassava yield variations under continuous cultivation of three crop mixtures in south-eastern Nigeria. Trop Agric. 2005;82:1–7.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

