The heme-regulated inhibitor kinase Hri1 is activated in response to aminolevulinic acid deficiency in Schizosaccharomyces pombe
- PMID: 40668850
- PMCID: PMC12303383
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011797
The heme-regulated inhibitor kinase Hri1 is activated in response to aminolevulinic acid deficiency in Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Abstract
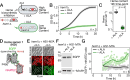
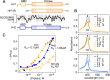
A key mechanism for regulating the initiation of protein synthesis in response to various stresses involves the phosphorylation of the α subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α). Schizosaccharomyces pombe possesses three distinct eIF2α kinases: Hri1, Hri2, and Gcn2. Using a strain that is unable to synthesize heme de novo (hem1Δ), global transcriptome analysis reveals that among the genes encoding these kinases, hri1+ is the most strongly induced under δ-aminolevulinate (ALA)-limiting conditions. The induction of hri1+ consistently correlates with increased eIF2α phosphorylation and a reduction in global protein translation in ALA-starved hem1Δ cells. In contrast, hem1Δ cells lacking hri1+ (hri1Δ) exhibit poor eIF2α phosphorylation under the same stress conditions. When ALA-starved hem1Δ hri1Δ cells are subsequently transferred to a medium supplemented with exogenous hemin, they exhibit impaired growth compared to ALA-starved hem1Δ cells expressing the endogenous hri1+ allele or hem1Δ hri1Δ hri2Δ gcn2Δ cells expressing functional hri1+ and hri1+-GFP alleles. Consistent with its role as a heme-sensing eIF2α kinase, further analysis by absorbance spectroscopy demonstrates that Hri1 binds to hemin, with an equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) of 0.11 µM. In contrast, a truncated form of Hri1 (from residues 1-185) fails to interact with hemin. Taken together, these findings provide the first report of a fungal eIF2α kinase being activated in response to stress directly linked to a defect in heme homeostasis.
Copyright: © 2025 Plante et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
New roles of the fission yeast eIF2α kinases Hri1 and Gcn2 in response to nutritional stress.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jul 15;126(Pt 14):3010-20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.118067. Epub 2013 May 17. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23687372
-
Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase Sty1 in regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinases in response to environmental stress in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Jan;9(1):194-207. doi: 10.1128/EC.00185-09. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 19880757 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 by heme-regulated inhibitor kinase-related protein kinases in Schizosaccharomyces pombe is important for fesistance to environmental stresses.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Oct;22(20):7134-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.20.7134-7146.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12242291 Free PMC article.
-
The protein kinases family in fungi: adaptability, virulence and conservation between species.Front Microbiol. 2025 Aug 15;16:1630196. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1630196. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40895487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

