Robot metabolism: Toward machines that can grow by consuming other machines
- PMID: 40668909
- PMCID: PMC12266095
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adu6897
Robot metabolism: Toward machines that can grow by consuming other machines
Abstract
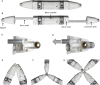
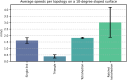
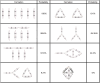
Biological lifeforms can heal, grow, adapt, and reproduce, which are abilities essential for sustained survival and development. In contrast, robots today are primarily monolithic machines with limited ability to self-repair, physically develop, or incorporate material from their environments. While robot minds rapidly evolve new behaviors through artificial intelligence, their bodies remain closed systems, unable to systematically integrate material to grow or heal. We argue that open-ended physical adaptation is only possible when robots are designed using a small repertoire of simple modules. This allows machines to mechanically adapt by consuming parts from other machines or their surroundings and shed broken components. We demonstrate this principle on a truss modular robot platform. We show how robots can grow bigger, faster, and more capable by consuming materials from their environment and other robots. We suggest that machine metabolic processes like those demonstrated here will be an essential part of any sustained future robot ecology.
Figures
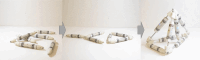




References
-
- Von Bertalanffy L., The theory of open systems in physics and biology. Science 111, 23–29 (1950). - PubMed
-
- Kanaev I. A., Evolutionary origin and the development of consciousness. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 133, 104511 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Lage C. A., Wolmarans D. W., Mograbi D. C., An evolutionary view of self-awareness. Behav. Processes 194, 104543 (2022). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

