Mechano-activated connexin hemichannels mediate intercellular glutathione transport and support lens redox homeostasis
- PMID: 40669209
- PMCID: PMC12283899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103767
Mechano-activated connexin hemichannels mediate intercellular glutathione transport and support lens redox homeostasis
Abstract
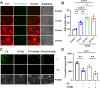
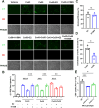
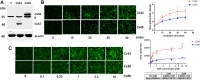
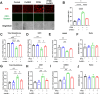
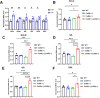
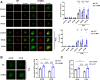
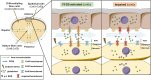
Redox homeostasis and transparency in the ocular lens are closely associated with the distribution of the antioxidant reduced glutathione (GSH). While the synthesis and recycling of GSH have been well characterized, the mechanisms governing its intercellular transport within the lens remain largely elusive. Here, we identified a GSH transport pathway mediated by connexin (Cx) hemichannels in both lens epithelial and fiber cells that has not been fully characterized previously. Through a combination of fluid flow shear stress (FFSS) stimulation, in vitro and ex vivo models, and gene knockout mouse models, we demonstrate that Cx43 and Cx50 hemichannels in lens epithelial cells facilitate GSH efflux in response to mechanical stimuli. Notably, Cx43 hemichannels exhibited higher opening efficiency and greater GSH transport capacity than Cx50 hemichannels under FFSS. The extracellular GSH released from epithelial cells was then taken up by activated Cx50 hemichannels in fiber cells under FFSS, effectively reducing oxidative stress and promoting cell survival. This intercellular relay of GSH between epithelial and fiber cells via mechanosensitive Cx hemichannels suggests a novel mechanism for regulating redox balance within the lens. This pathway may be essential for preserving lens homeostasis and offers new insight into lens physiology and potential therapeutic strategies for preventing or delaying cataract formation.
Keywords: GSH; Hemichannels; Lens; Redox homeostasis.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Declarations of interest for all authors: none.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechano-activated connexin hemichannels and glutathione transport protect lens fiber cells against oxidative insults.Redox Biol. 2024 Jul;73:103216. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103216. Epub 2024 May 28. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38820983 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin hemichannels mediate glutathione transport and protect lens fiber cells from oxidative stress.J Cell Sci. 2018 Mar 21;131(6):jcs212506. doi: 10.1242/jcs.212506. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29487175 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensitive collaboration between integrins and connexins allows nutrient and antioxidant transport into the lens.J Cell Biol. 2020 Dec 7;219(12):e202002154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202002154. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 33180092 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin-43 remodelling and arrhythmias: hemichannels as key drivers of cardiac dysfunction.J Physiol. 2025 Aug;603(15):4293-4306. doi: 10.1113/JP288091. Epub 2025 May 5. J Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40320914 Review.
-
Gap junction connexins in female reproductive organs: implications for women's reproductive health.Hum Reprod Update. 2015 May-Jun;21(3):340-52. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv007. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Hum Reprod Update. 2015. PMID: 25667189
References
-
- Giblin F.J. Glutathione: a vital lens antioxidant. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2000;16:121–135. - PubMed
-
- Lou M.F. Thiol regulation in the lens. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2000;16:137–148. - PubMed
-
- Ganea E., Harding J.J. Glutathione-related enzymes and the eye. Curr. Eye Res. 2006;31:1–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

