The role of lipid metabolism imbalance in copper-induced PANoptosis in broiler kidney
- PMID: 40669240
- PMCID: PMC12284046
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105549
The role of lipid metabolism imbalance in copper-induced PANoptosis in broiler kidney
Abstract
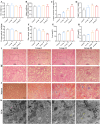
Copper (Cu) is widely used in both agriculture and industry and may pose toxic risks to animals and public safety if overused. In order to gain a more profound insight into the nephrotoxic effects of Cu, a detailed analysis was performed of its impact on renal PANoptosis, with particular attention being paid to the possible involvement of lipid metabolism disorders in the kidney. In this study, one-day-old chicks were fed diets with varying Cu levels (11, 110, 220, and 330 mg/kg) over a period of 49 days. Our findings indicated that excessive Cu exposure led to vacuolar degeneration, fibrosis and mitochondrial damage in the kidney. Moreover, the assay results demonstrated that elevated Cu levels led to disturbances in lipid synthesis and catabolism, as well as the activation of lipophagy in broiler kidneys. Concurrently, genetic and protein analysis demonstrated that excess Cu triggered pyroptosis (IL-18, NLRP3, GSDMD, Caspase-1), necrosis (MLKL, Caspase-7, Caspase-8) and apoptosis (Bcl-2, Cleaved-Caspase-9/Caspase-9, Cleaved-Caspase-9/Caspase-9), ultimately resulting in PANoptosis in the chicken kidney. Furthermore, the bioinformatics analysis indicated a correlation between lipid metabolism and PANoptosis-related markers. The aforementioned results indicate that Cu-induced disruption to lipid metabolism may contribute to the process of PANoptosis in broiler kidneys.
Keywords: Broiler; Copper; Kidney; Lipid metabolism; PANoptosis.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Ai Y., Meng Y., Yan B., Zhou Q., Wang X. The biochemical pathways of apoptotic, necroptotic, pyroptotic, and ferroptotic cell death. Mol. Cell. 2024;84:170–179. - PubMed
-
- Casanova A.G., Hinojosa M.G., Chamorro-López C., Martín-Reina J., Aguilera-Velázquez R., Bautista J.D., Morales A.I., Moreno I.M. Oxidative stress and renal status of farmers exposed to pesticides in Seville (Spain) Sci. Total Environ. 2024;951 - PubMed
-
- Chen L., Zhou M., Wang J., Zhang Z., Duan C., Wang X., Zhao S., Bai X., Li Z., Li Z., Fang L. A global meta-analysis of heavy metal(loid)s pollution in soils near copper mines: Evaluation of pollution level and probabilistic health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;835 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

