The extracellular vesicle transcriptome provides tissue-specific functional genomic annotation relevant to disease susceptibility in obesity
- PMID: 40669467
- PMCID: PMC12534702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2025.100925
The extracellular vesicle transcriptome provides tissue-specific functional genomic annotation relevant to disease susceptibility in obesity
Abstract
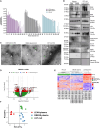
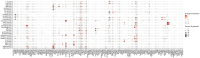
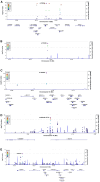
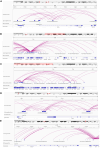
We characterized circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs) in obese and lean humans, identifying transcriptional cargo differentially expressed in obesity (277 unique genes; false discovery rate < 10%). Since circulating EVs may have broad origin, we compared this obesity EV transcriptome with expression from human visceral-adipose-tissue-derived EVs from freshly collected and cultured biopsies from the same obese individuals, observing high concordance. Using a comprehensive set of adipose-specific epigenomic and chromatin conformation assays, we found that the differentially expressed transcripts from the EVs were those regulated in adipose by body mass index-associated SNPs (p < 5 × 10-8) from a large-scale genome-wide association study (GWAS). Using a phenome-wide association study of the regulatory SNPs for the EV-derived transcripts, we identified a substantial enrichment for inflammatory phenotypes, including type 2 diabetes. Collectively, these findings represent the convergence of the GWAS (genetics), epigenomics (transcript regulation), and EV (liquid biopsy) fields, enabling powerful future genomic studies of complex diseases.
Keywords: BMI; GWAS; PheWAS; RNA; extracellular vesicles; obesity; plasma; visceral adipose tissue.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.S. is supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. R.S. has equity ownership in and is a consultant for Thryv Therapeutics. R.S. is a co-inventor on pending patents or disclosures on molecular biomarkers of fitness, lung disease, cardiovascular diseases and phenotypes, and metabolic health; use of RNAs as therapeutics and diagnostic biomarkers in disease; and methods in metabolomics. E.R.G. is a consultant for Thryv. He is a co-inventor on disclosures or patents on cardiovascular diseases and phenotypes and metabolic health, use of RNAs as therapeutics and diagnostic biomarkers in disease, and methods in metabolomics. S.D. is a cofounder and consultant and has equity in Thryv Therapeutics and Switch Therapeutics, neither of which played a role in this study.
Figures



Update of
-
The extracellular vesicle transcriptome provides tissue-specific functional genomic annotation relevant to disease susceptibility in obesity.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 18:2024.11.18.24317277. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.18.24317277. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Genom. 2025 Sep 10;5(9):100925. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2025.100925. PMID: 39606385 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Speliotes E.K., Willer C.J., Berndt S.I., Monda K.L., Thorleifsson G., Jackson A.U., Lango Allen H., Lindgren C.M., Luan J., Mägi R., et al. Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:937–948. doi: 10.1038/ng.686. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

