Effectiveness of exercise therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis: an overview of systematic reviews
- PMID: 40669904
- PMCID: PMC12273085
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093163
Effectiveness of exercise therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis: an overview of systematic reviews
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the methodological quality of published systematic reviews of exercise therapy in knee osteoarthritis and summarise their reported effectiveness on quality of life, knee joint function, or adverse events.
Design: Overview of systematic reviews.
Data sources: PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, Web of Science and CENTRAL (searched on 14 April 2025), plus grey literature (PROSPERO, Epistemonikos, OpenGrey).
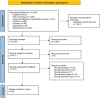
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: We included systematic reviews of randomised controlled trials in patients diagnosed with knee osteoarthritis by imaging or clinical criteria and treated conservatively with exercise therapy; we excluded reviews that enrolled patients scheduled for surgery, with acute inflammation or osteoarthritis of other joints (hand, hip, ankle), for which relevant author data could not be obtained after one contact attempt, or that did not report at least one primary outcome (quality of life, knee joint function or adverse events).
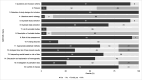
Data extraction and synthesis: Two reviewers independently extracted data on study characteristics, interventions and outcomes, and assessed methodological quality using the AMSTAR 2 (A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews 2) tool. Due to heterogeneity in outcome measures across systematic reviews, meta-analysis was not conducted. Effectiveness was defined as any reported beneficial outcome of exercise therapy on predefined outcomes, including quality of life, physical function, pain or adverse events.
Results: 58 systematic reviews were selected. Muscle-strengthening (74.1%) and aerobic (48.2%) exercises were the most commonly prescribed exercise-based interventions. SF-36 (36-Item Short Form Health Survey) and the WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) were the most popular outcome-evaluation tools. Furthermore, 63.7% of the systematic reviews revealed that exercise therapy improved all outcomes. The number of intervention-related adverse events was small. Notably, almost all systematic reviews (87.4%) had a critically low quality.
Conclusions: Current evidence on exercise therapy for knee osteoarthritis is inadequate. Nevertheless, exercise therapy can be considered for conservative treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Future studies should use network meta-analyses to compare the effects of different exercise therapies and determine their superiority over other conservative therapies.
Keywords: Exercise; Knee; Physical Fitness; Quality of Life; Systematic Review.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physical activity and exercise for chronic pain in adults: an overview of Cochrane Reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 24;4(4):CD011279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011279.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28436583 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity and exercise for chronic pain in adults: an overview of Cochrane Reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 14;1(1):CD011279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011279.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 24;4:CD011279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011279.pub3. PMID: 28087891 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Exercise interventions and patient beliefs for people with hip, knee or hip and knee osteoarthritis: a mixed methods review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD010842. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010842.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664187 Free PMC article.
-
Adjunctive therapies in addition to land-based exercise therapy for osteoarthritis of the hip or knee.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 17;10(10):CD011915. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011915.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36250418 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic acid and other conservative treatment options for osteoarthritis of the ankle.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 17;2015(10):CD010643. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010643.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26475434 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous