Evaluation of strength, skin temperature and muscle activation in traditional and eccentric training in Paralympic Powerlifting athletes
- PMID: 40670545
- PMCID: PMC12267619
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-10530-z
Evaluation of strength, skin temperature and muscle activation in traditional and eccentric training in Paralympic Powerlifting athletes
Abstract
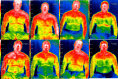
Paralympic Powerlifting (PP) is a maximum strength modality, where male athletes demonstrated greater relative and absolute strength compared to conventional powerlifting. This study aimed to assess the acute effects of traditional training (TT) and eccentric training (ET) methods on Maximum Isometric Strength (MIF), Time to Maximum Isometric Force (Time), Muscle Activation (sEMG), and Skin Temperature (Thermo) in twelve male PP athletes (mean age 30.25 ± 8.13; body weight 72.36 ± 18.47). The training consisted of 5 sets of 5 repetitions (5 × 5), with 80% 1RM in the TT method and in the ET 80% was adopted in the concentric phase and 110% in the eccentric phase, adopting a minimum rest of 3 min between sets and the cadence used was approximately 2 s in the eccentric phase and 1 s in the concentric phase for the ET and 1 s in each phase for the TT. Athletes competing nationally and internationally underwent Thermo, Time, and MIF assessments during TT (80%-1RM for both concentric and eccentric phases) and ET (80%-1RM concentric and 110%-1RM eccentric) at pre-training, post-training, 24 h, and 48 h. sEMG was evaluated in the clavicular portion of the pectoralis major (PMCP), sternal portion of the pectoralis major (PMSP), anterior Deltoid (AD), and Triceps Brachii (BT) during the final series (5 sets of 5 repetitions) of a training session. Athletes exhibited thermal differences in the PMCP muscle at 24 h between TT and ET (p = 0.020); Also, after the first 24 h, the AD showed differences between ET and TT (p = 0.016) and BT demonstrated differences between ET and TT (p = 0.028). The sEMG showed no significant differences between TT and ET (p > 0.05). The MIF displayed differences after 48 h between TT and ET (p = 0.004). The time showed no significant difference between TT and ET (p > 0.05). In conclusion, muscles involved in the bench press exhibited a significant increase in skin temperature with the ET method compared to TT, suggesting greater muscular fatigue. Furthermore, a higher MIF production was observed after the application of the TT in relation to ET, 48 h after training. In the ET, a lower MIF was observed than in the TT, indicating greater fatigue in this type of training.
Keywords: Muscle strength; Paralympic Powerlifting; Strength training; Surface electromyography; Thermography.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board and approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Sergipe (UFS), under Statement Number 2637882/2018.Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dose-Response Relationships of Resistance Training in Healthy Old Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2015 Dec;45(12):1693-720. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0385-9. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26420238 Free PMC article.
-
Myoelectric activity during electromagnetic resistance alone and in combination with variable resistance or eccentric overload.Sci Rep. 2023 May 22;13(1):8212. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35424-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37217559 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Flat-Back vs. Arched-Back Bench Press: Examining the Different Techniques Performed by Power Athletes.J Strength Cond Res. 2024 Jul 1;38(7):1200-1205. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000004778. Epub 2024 Mar 29. J Strength Cond Res. 2024. PMID: 38551927 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Strength Development in Traditional Set-Repetition Configuration Versus Accentuated Eccentric Loading Training over a 4-Week Strength-Endurance Block.J Strength Cond Res. 2025 May 16;39(8):850-856. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000005135. J Strength Cond Res. 2025. PMID: 40440528 Clinical Trial.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WPPO Rules and Regulations_2022_v1.4_0.pdf [Internet]. Disponível em: https://www.paralympic.org/sites/default/files/2023-07/WPPO%20Rules%20an... (2025).
-
- van den Hoek, D. et al. Analysis of competition performance leading to success at the international powerlifting federation world championships between 2013 and 2019. J. Strength Cond. Res.37(10), e555–e562 (2023). - PubMed
-
- van den Hoek, D., Garrett, J., Howells, R. & Latella, C. Paralympians are stronger than you know: A comparison of para and nondisabled powerlifting bench press world records. J. Strength Cond. Res.37(2), 452–456 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Levantamento de peso paralímpico como uma maneira sustentável de melhorar a força em atletas com lesão medular e outras deficiências [Internet]. Disponível em: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/4/2017 (2025).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

