Effect of sterilization on the cutting efficiency of two different rotary NiTi instruments (An In- vitro Study)
- PMID: 40671008
- PMCID: PMC12269300
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-06534-w
Effect of sterilization on the cutting efficiency of two different rotary NiTi instruments (An In- vitro Study)
Abstract
Background: Dental rotary instruments can be applied under multiple canal conditions. This study assessed the performance of two batches of NiTi dental rotary files-Mani Jizai (Jz) and Dentsply ProTaper Next (PTN)-by evaluating their cutting efficiency.
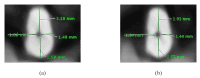
Methods: A total of 80 files (40 from each type), with 8x digital microscope magnification used for defect inspection, were tested half of which before and the other half after sterilization. The sample size was tested in extracted upper molars' distobuccal (DB) roots to assess cutting efficiency by volumetric changes showing removed dentin volume.
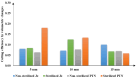
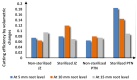
Results: The Results indicated that the sterilized PTN files performed better at 5 mm, but no significant differences were noted at 10 mm between all file groups. At 15 mm, the performance of sterilized PTN files was inferior to that of non-sterilized Jz files.
Conclusion: Sterilization and heat treatment affect file cutting efficiency by volumetric changes, especially at the coronal and apical one-thirds.
Keywords: Cutting efficiency; NiTi; Rotary files; Sterilization.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethics approval was obtained from the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Dentistry Ain Shams University (Reference number: FDASU-Rec EM112308). The need for informed consent was deemed unnecessary by the ethics committee of the Faculty of Dentistry, Ain Shams University according to national regulations since the extracted molars were collected from anonymous patients who consented to the use of their extracted teeth for research purposes. All methods were carried out following relevant guidelines and regulations. The study adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pedullà E, Benites A, La Rosa GM, Plotino G, Grande NM, Rapisarda E, et al. Cyclic fatigue resistance of Heat-treated Nickel-titanium instruments after immersion in sodium hypochlorite and/or sterilization. J Endod. 2018;1(4):648–53. 10.1016/j.joen.2017.12.011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

